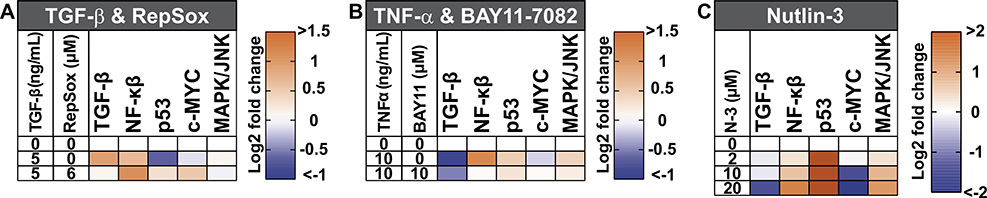
Figure 12. Multiplex luciferase analysis of effects of different ligand and drug treatments on signaling pathways in mammalian A549 lung cancer cells.
(A) The TGF-β pathway is one-fold activated after adding recombinant TGF-β ligand (5 ng/mL), but TGF-β also causes significant collateral activation of the NF-κβ and downregulation of the p53 pathways. Simultaneous addition of downstream RepSox inhibitor (6 μM) neutralizes the effects of recombinant TGF-β addition on TGF-β and p53 pathway signaling, while significantly activating the NF-κβ and c-MYC pathways. Changes in the other monitored pathways are non-significant. (B) The NF-κβ pathway is 1.5-fold activated after treatment with recombinant TNF-α ligand (10 ng/ml), but also has a strong downregulating effect in the TGF-β pathway. Simultaneous treatment with the downstream NF-κβ pathway inhibitor BAY11–7082 (10 μM) neutralizes the effect of recombinant TNF-α on the NF-κβ pathway and attenuates the downregulation of the TGF-β pathway. Changes in the other monitored pathways are non-significant. (C) Increasing concentrations of Nutlin-3 (N-3), from 2 to 20 μM, result in a strong activation of the p53 pathway, and incremental activation of the NF-κβ and MAPK/JNK pathways. At 10 μM, Nutlin-3 strongly downregulates the c-MYC pathway, and, at 20 μM, Nutlin-3 strongly downregulates the TGF-β and c-MYC pathways.