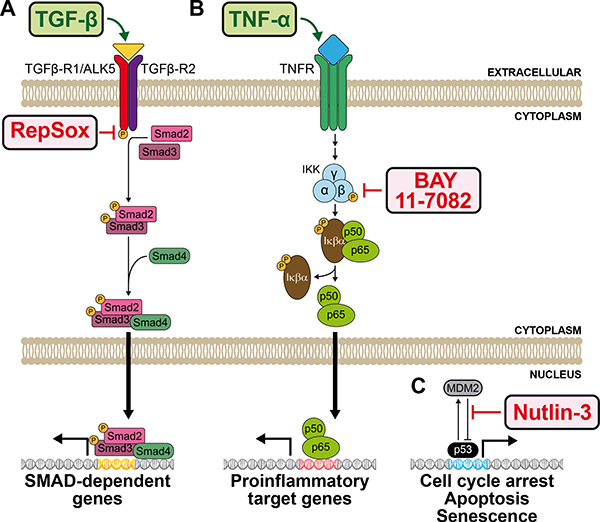
Figure 5. Pathway schematics of pharmaceutical and ligand interventions of three signaling pathways known to be active in mammalian A549 cells.
(A) Simplified schematic of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) pathway. The ligand TGF-β (GeneCards ID: TGFB), binds its heterodimeric receptor (GeneCards ID: TGFBR1 and TGFBR2), resulting in the downstream activation of the signal transducing and transcriptional modulating SMAD cascade (GeneCards IDs: SMAD2, 3, and 4), subsequently followed by the transcriptional upregulation of SMAD-dependent genes. The TGF-β pathway-activating ligand is labelled in green, while the TGF-β pathway inhibiting pharmaceutical (RepSox) is labelled in red. (B) Simplified schematic of the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) pathway. The ligand TNF-α (GeneCards ID: TNF) binds its trimeric receptor, consisting of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily members 1A and 1B proteins (GeneCards IDs: TNFRSF1A or TNFRSF1B), resulting in the downstream phosphorylation of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, consisting of α/IKK-α (GeneCards ID: CHUK), β/IKK-β (GeneCards ID: IKBKB), and γ/IKK-γ (GeneCards ID: IKBKG). The IKK complex then activates the NF-κβ protein complex consisting of IκΒα/ nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (GeneCards ID: NFKBIA), p50/ Nuclear Factor NF-Kappa-B P50 Subunit (GeneCards ID: NFKB1), and p65/Nuclear Factor NF-Kappa-B P65 Subunit (GeneCards ID: RELA), through phosphorylation and release of IκΒα. The liberated p50/65 complex then transports to the nucleus followed by the transcriptional upregulation of proinflammatory target genes. The TNF-α pathway-activating ligand is labelled in green, while the TNF-α pathway inhibiting pharmaceutical (BAY11–7082) is labelled in red. (C) Simplified schematic of p53 pathway activation induced by Nutlin-3. Nutlin-3 selectively inhibits the interaction between the ubiquitin-protein ligase called mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) homolog (GeneCard ID: MDM2), and tumor protein p53 (GeneCard ID: TP53), resulting in p53 pathway activation. The p53 pathway inhibiting pharmaceutical (Nutlin-3) is labelled in red.