Fig. 1. Absorption detection of single nanoparticles using optical forces.
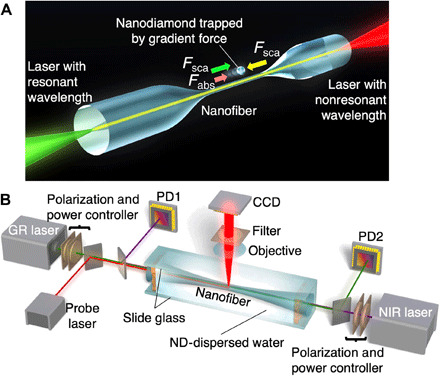
(A) Concept of optical force absorption spectroscopy. By monitoring the mechanical motion of a single nanoparticle driven by optical forces, the resonant absorption properties can be analyzed with high sensitivity. Using two different-colored lasers counterpropagating along a nanofiber, a nanoparticle is trapped by the gradient force and transported by the absorption and scattering forces. The laser powers are adjusted to cancel out the scattering forces such that the particle moves depending on the absorption cross section. (B) Experimental setup. GR and NIR diode lasers are introduced from both ends of a nanofiber. The laser powers are measured by photodiodes (PD1 and PD2) and controlled by rotational neutral density filters to balance the forces. To record the motion of nanoparticles, a weak red laser is used, and its scattered light is monitored using a microscope-attached charge-coupled device (CCD) camera with filters to cut the strong scattered light of the GR and NIR lasers.
