Fig. 1. Late up-regulation of EGR1 during macrophage differentiation results in EGR1 binding at distal genomic regions.
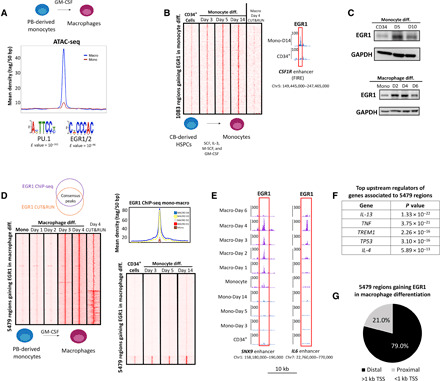
(A) ATAC-seq profile of top 5000 macrophage-specific peaks (ranked on the basis of adjusted P value) shows increased accessibility in macrophages after treatment with GM-CSF to promote differentiation from peripheral blood (PB)–derived monocytes. Motif analysis at these regions shows PU.1- and EGR1/EGR2-binding motifs as the most significantly enriched. (B) CUT&RUN heatmap shows that 1083 genomic sites gain EGR1 binding during monocyte differentiation from bone marrow–derived HSPCs. These sites include the FIRE enhancer of the CSF1R gene. (C) Immunoblot data reveal that EGR1 protein levels are up-regulated early during monocyte differentiation from HSPCs. Conversely, EGR1 is up-regulated after 3+ days of macrophage differentiation and quickly down-regulated past day 4. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (D) Genomic data support a late up-regulation of EGR1 during macrophage differentiation. On the basis of ChIP-seq– and CUT&RUN-replicated experiments, 5479 genomic regions gain EGR1 binding during macrophage differentiation. These 5479 regions are replicated across time ponts (day 3 and day 4) and between methodologies (ChIP-seq and CUT&RUN). Moreover, the 5479 regions specific to the macrophage lineage show limited overlap by EGR1 during monocyte differentiation from CD34+ cells. (E) CUT&RUN genome browser tracks show examples of enhancer regions occupied by EGR1 through macrophage differentiation. Shown are enhancers associated with SNX9 and the cytokine IL-6. (F) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis shows that genes associated to EGR1-gaining regions share upstream regulators involved in immune response pathways. (G) The very large majority of EGR1-gaining regions are distal (i.e., >1 kb from transcription start sites), suggesting that they are putative enhancers. All heatmaps displayed are from one replicate and are normalized by sequencing depth.
