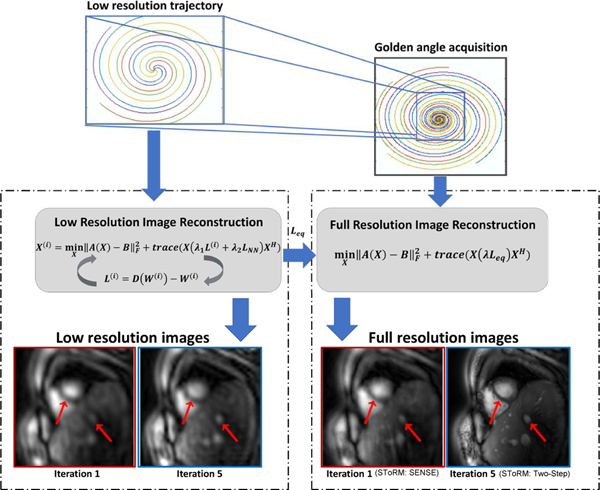
Fig. 1:
Outline of the SToRM: Two-Step method. Free-breathing and ungated data is acquired using golden angle interleaved spiral trajectories. We rely on a two-step strategy, where a low-resolution dataset is first recovered from the central k-space regions denoted by the blue box. Since this region is still not fully sampled, kernel low-rank regularization is used to recover the images. As described in the text, this iterative strategy yields the Laplacian matrix as a by-product. Once the Laplacian is available, the high-resolution dataset is estimated from all of the k-space samples by solving Eq. (9). The first image with red border in the left panel corresponds to the low-resolution image recovered by the first iteration of the kernel low-rank algorithm, which corresponds to a SToRM:SENSE method. The Laplacian matrix estimated from this result (iteration 1 with red border) is used to recover the high-resolution data, indicated by the first image with a red border in the right panel. By contrast, iterating the kernel low-rank algorithm provides more details, as shown by the second image in the left panel with a blue border. The recovery using the Laplacian from this estimate, termed as SToRM:Two-Step, yields improved image quality, as shown in the second image in the right panel with a blue border.