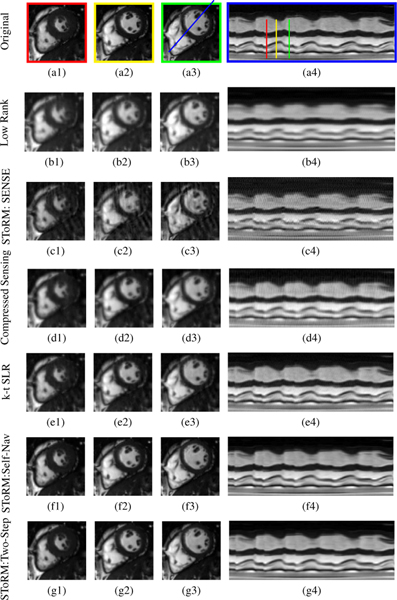
Fig. 3:
Performance of the algorithm using a simulated short-axis cardiac cine dataset. We compare the low-rank algorithm (b1-b3), SToRM: SENSE method (c1-c3), the compressed sensing method (d1-d3), k-t SLR (e1-e3), SToRM: Self-Nav (f1-f3) and the proposed method (g1-g3). Each scheme (k-t or non-binning method) is compared against the original dataset (a1-a3). This dynamic dataset is retrospectively undersampled using a golden angle spiral sampling pattern. Three cardiac phases are picked from each reconstruction method and correspond to end of systolic, mid phase, and end of diastolic, as shown by red, yellow, and green lines in the time profile (a4). The time profiles in the last column are shown for the entire time series, along the line passing through the left ventricle and right ventricle shown in (a3). We observe that the proposed method provides reconstructions with lower spatial and temporal blurring compared to low-rank, SToRM:SENSE, k-t SLR and compressed sensing methods. It gives comparable image quality to SToRM:Self-Nav. Table I shows a quantitative comparison of the methods using SER, HFEN, SSIM, and GPC metrics computed around the cardiac region.Since XD-GRASP uses different reconstruction strategy,so we have done separate comparison with XD-GRASP method.