Fig. 2.
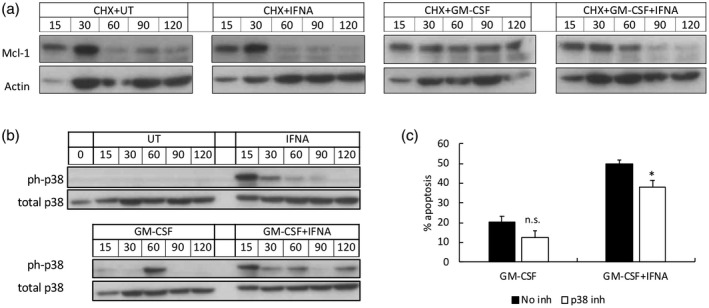
The effect of interferon (IFN‐α) on myeloid cell leukaemia 1 (Mcl‐1) turnover and p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation. (a) Preincubation of neutrophils with cycloheximide prior to granulocyte–macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) and IFN‐α showed increased turnover of Mcl‐1 protein levels in the presence of IFN‐α, probably through blockade of Mcl‐1 protein stabilization. (b) p38 MAPK was rapidly phosphorylated by IFN‐α over 120 min in the absence and presence of GM‐CSF. (c) Inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation by BIRB796 significantly inhibited the abrogative effect of IFN‐α on GM‐CSF‐delayed neutrophil apoptosis over 18 h (n = 4, *P < 0·05, n.s. = not significant).
