Fig. 3.
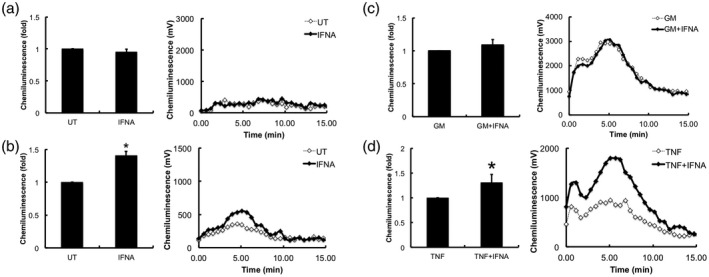
Effect of interferon (IFN‐α) on neutrophil respiratory burst. Neutrophils were incubated with cytokines for 4 h and at hourly time‐points, samples were removed and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in response to f‐Met‐Leu‐Phe (fMLP) (1 μM) was measured over 15 min. (a) IFN‐α (IFNA) did not prime the respiratory burst in response to fMLP after short incubation times of 1 h, (b) but did significantly prime the respiratory burst after 3 h incubation. (c) Co‐incubation of IFN‐α with granulocyte macrophage–colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) had no effect on neutrophil priming for up to 4 h. (d) IFN‐α maintained TNF‐induced priming for up to 4 h incubation. Representative traces from four experiments (*P < 0·05, **P < 0·01).
