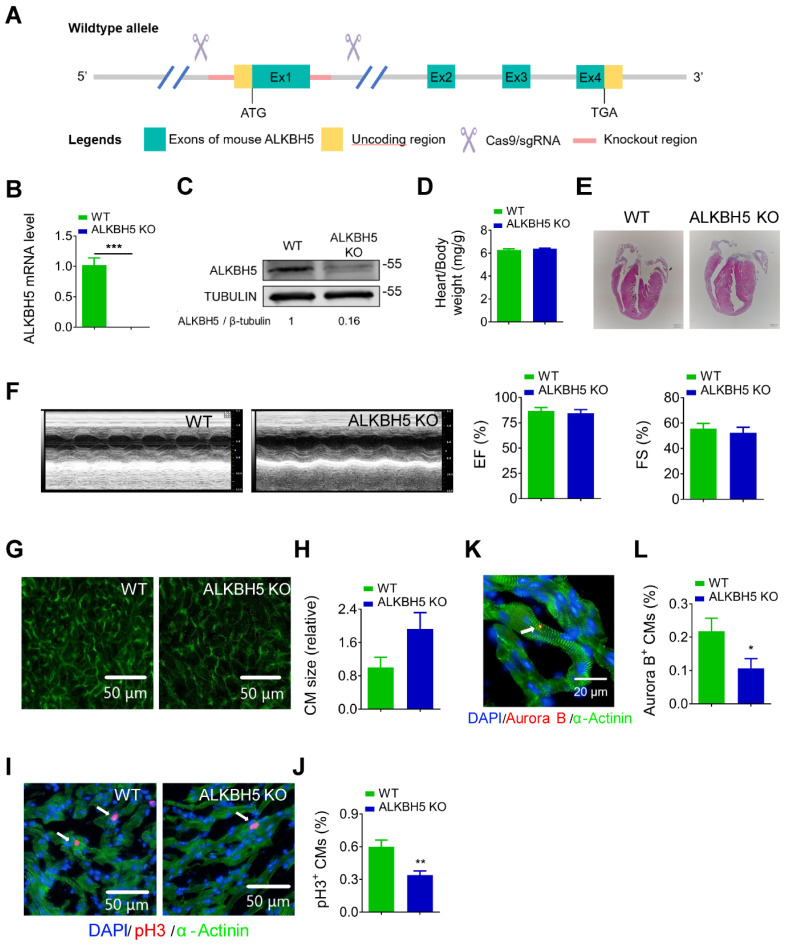
Figure 3.
Deletion of ALKBH5 inhibits cardiomyocyte proliferation in vivo. (A) Schematic for generating transgenic ALKBH5 KO mice. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of ALKBH5 in hearts from P21 WT and ALKBH5 KO mice (***P < 0.001, n = 4). (C) Western-blot analysis of ALKBH5 in hearts from P21 WT and ALKBH5 KO mice. β-TUBULIN was used as a loading control. (D) Heart weight to body weight ratio of ALKBH5 KO mice and wild-type (WT) mice (n = 5). (E) HE staining of heart from 1 month-old ALKBH5 KO mice and wild-type (WT) mice. (F) Cardiac function analyzed by echocardiography. EF, ejection fraction FS, fraction shortening. (G-H) Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining and quantification of P21 ALKBH5 KO (n = 8) and wild-type (WT) (n = 6) hearts. Scale bars, 50 µm. (I, J) pH3 immunofluorescence staining in P21 ALKBH5 KO and wild-type (WT) hearts and quantification of pH3-positive CMs (22587 CMs in the WT group and 10397 CMs in the ALKBH5 KO group). **P < 0.01. (K, L) Aurora B kinase immunofluorescence staining in P21 ALKBH5 KO and wild-type (WT) hearts and quantification of pH3-positive CMs (13844 CMs in the WT group and 16411 CMs in the ALKBH5 KO group). *P < 0.05. Scale bar, 20 µm.