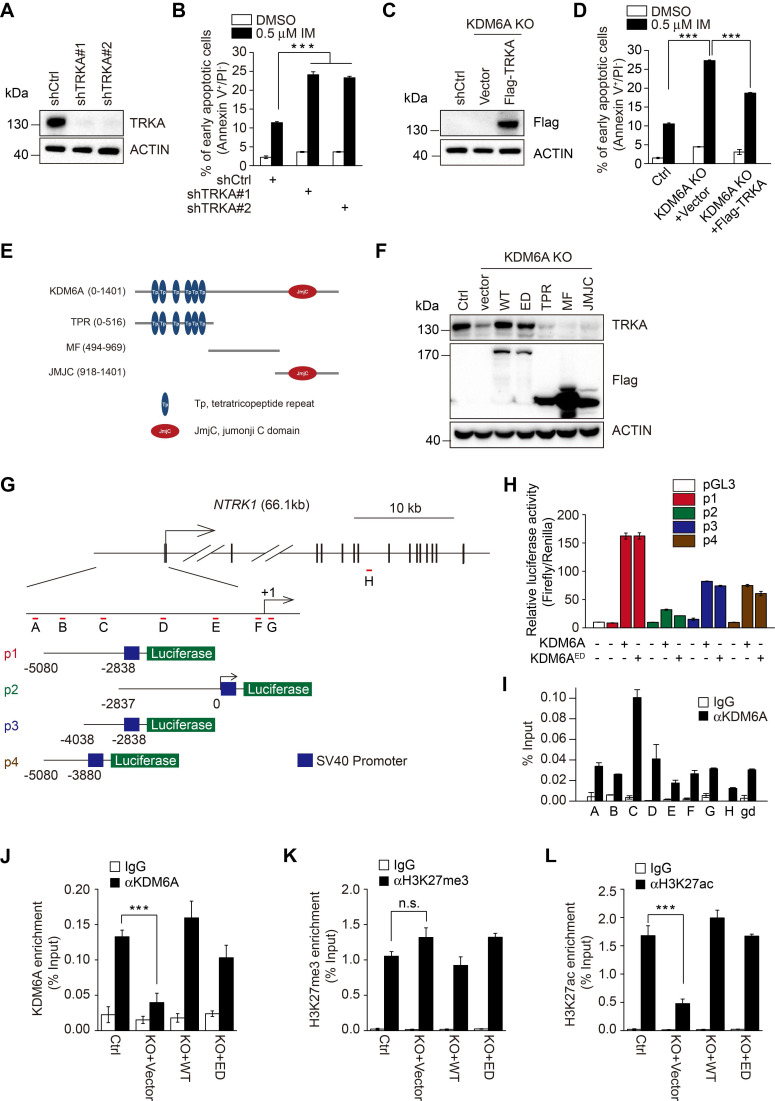
Figure 4.
KDM6A promotes imatinib-resistance through transcriptional activation of NTRK1. (A) Knockdown efficiency of two independent shRNAs targeting TRKA in K562 cells as determined by Western blot. (B) The rates of early apoptosis in shCtrl versus shTRKA K562 cells were determined by FACS after treatment with 0.5 μM imatinib for 24 h. Mean ± s.d. are given for three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA; ***p < 0.001. (C, D) Western blot showing stable expression of Flag-TRKA but not Flag vector control restores TRKA expression in K562 KDM6A KO#2 cells (C) and significantly decreases their imatinib sensitivity (D) as shown by decreases in apoptotic cells after treatment with 0.5 μM imatinib for 24 h. Mean ± s.d. are given for three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA; ***p < 0.001. (E, F) Schematic diagram of KDM6A protein (top) and the design of domain truncation mutants (bottom; E). Flag-tagged versions wild-type KDM6A (WT), an enzyme-dead mutant of KDM6A (ED) or the KDM6A truncation mutants along with a flag-vector control were used as lentiviral constructs to stably infected KDM6A KO#2 cells (F). The expression of transduced proteins was revealed by Western blotting against Flag along with changes in TRKA expression. (G) Promoter region and intron/exon organization of NTRK1. Schematic shows the four overlapping fragments (p1, p2, p3 and p4) used to construct pGL3-promoter based luciferase reporters along with the position of the amplicon targets (A-H) used in ChIP-qPCR assays. (H) Luciferase reporter assays conducted in U2OS cells transfected with the indicated pGL3-NTRK1 reporter vectors from (G) in combination with KDM6A or KDM6A-ED. (I) ChIP-qPCR analyses against the NTRK1 gene using the amplicon targets shown in (H) along with a control gene desert sequence (gd) Chr2(q36.3). Assays were performed in K562 cells using either control IgG or anti-KDM6A antibody. Mean ± s.d. are given for three independent experiments. Unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test; ***p < 0.001. (J-L) ChIP-qPCR assays were conducted as per (I) against KDM6A (J), H3K27me3 (K), or H3K27ac (L) against amplicon targets C, comparing parental K562 cells (Ctrl) against KDM6A KO#2 cells reconstituted with vector (KO+vector), KDM6A (KO+WT) or KDM6A-ED (KO+ED). (A-D, F, H-L) represent three independent experiments. Mean ± s.d. are given for three independent experiments. Unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test; ***p < 0.001; n.s., not significant.