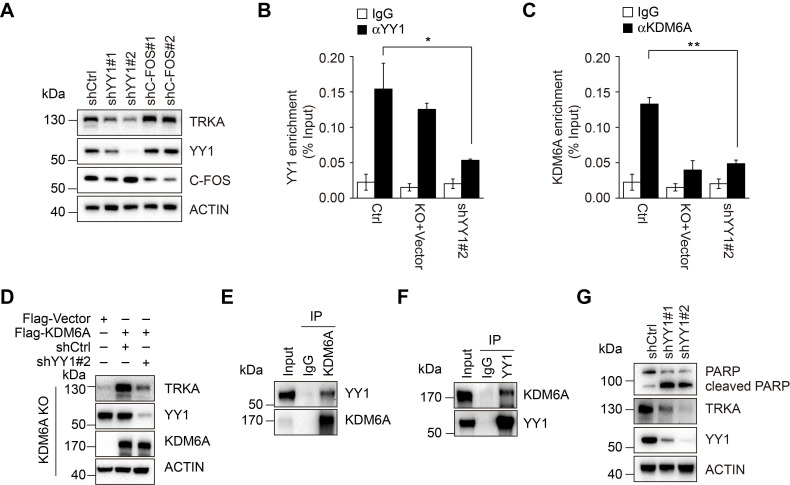
Figure 5.
YY1 is necessary for KMD6A-mediated NTRK1 transcription. (A) Western blot analysis showing knockdown of YY1 but not c-Fos by lentiviral-mediated shRNA transduction decreased TRKA protein expression in K562 cells. (B, C) ChIP-qPCR assays were conducted using antibodies against YY1 (B) or KDM6A (C) in control K562 versus KDM6A-KO cells or cells expressing shRNA against YY1. Target amplicons targeting C region are illustrated in Fig. 4G. KDM6A-KO failed to significantly reduce recovery of YY1 ChIP signals at the NTRK1 enhancer region (B) whereas conversely YY1 knockdown reduced KDM6A ChIP target recovery (C). Mean ± s.d. are given for three independent experiments. Unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test; *p <0.05. (D) Western blot analysis showing re-constitution of TRKA expression in KDM6A KO K562 cells requires YY1. (E, F) Immunoprecipitation analyses conducted against KDM6A (E) or YY1 (F) in K562 cells demonstrates reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation between KDM6A and YY1. IgG was used as a control. (G) Western blot analysis showing increased PARP cleaved in K562 cells after treatment with 1 μM imatinib IM for 48 h when YY1 is depleted.