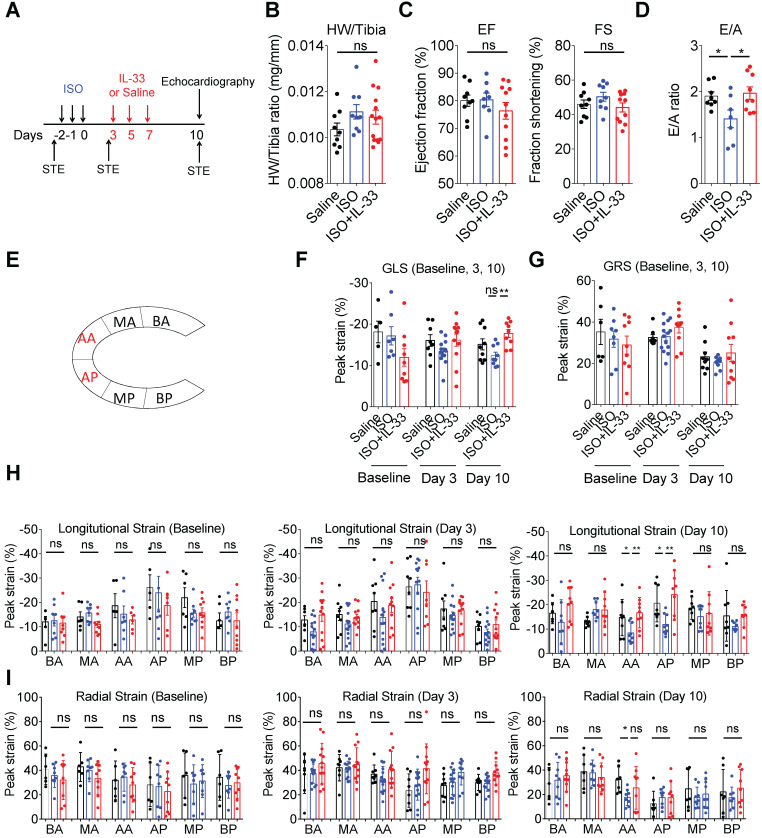
Figure 4.
IL-33 treatment prevents ISO-induced progressive cardiac function impairment. (A) BALB/cByJ mice were subcutaneously administered isoproterenol (ISO) (60 mg/kg) for three days followed by intraperitoneal Saline or IL-33 (0.5 μg/mouse) treatment on days 3, 5, and 7. Cardiac functions were evaluated by M-mode echocardiography (on day 10), pulse wave Doppler (on day 10), and speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE, on day -3 before ISO challenge as baseline, day 3 after the last ISO injection before IL-33 or saline administration, and day 10 post-ISO challenge) (n = 6-10 per group) before the mice were euthanized (SAC). (B) Heart weight to tibia length ratio of the mice between groups. (C) Analysis of the ejection fraction (EF) and fraction shortening (FS) by M-mode echocardiography. (D) Pulse wave Doppler analysis of the ratio of peak velocity of early to late filling of mitral inflow (E/A) (E) Schematic overview of anatomical segments in the parasternal long-axis view. Anterior (AA) and posterior (AP) apex; anterior (BA) and posterior (BP) base; anterior (MA) and posterior (MP) mid. (F) Quantification of the global longitudinal strain (GLS) and (G) global radial strain (GRS) of the mice. (H) Quantification of the segmental longitudinal peak strain upon ISO and IL-33 treatment. (I) Quantitative analysis of segmental radial peak strain. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison post-hoc test. All values are means ± SD. Each dot indicates a biological replicate. *P < 0.05, **P<0.01 by one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison post-hoc test.