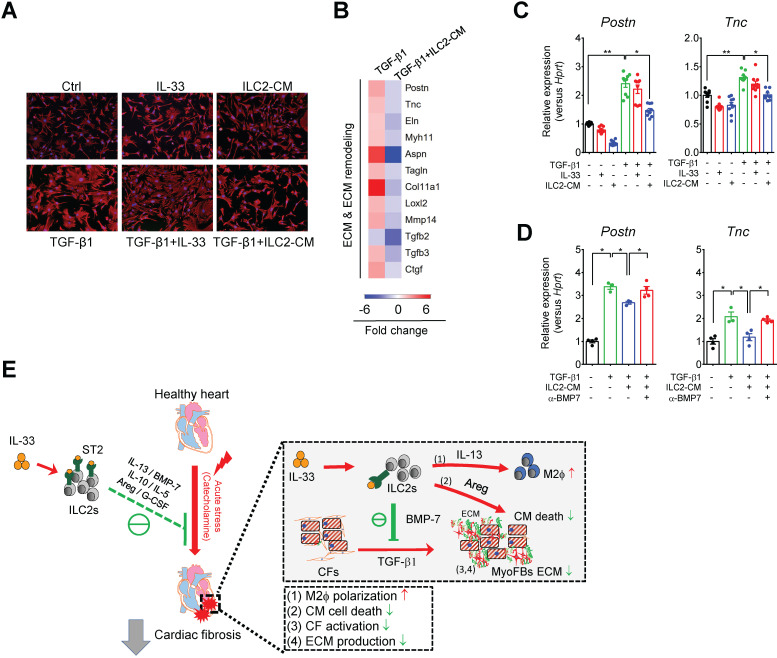
Figure 8.
ILC2-derived factors inhibit TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation. (A) Primary mouse cardiac fibroblasts were cultured with Saline IL-33 (30 ng/mL) or ILC2-conditioned media (ILC2-CM, 1:100 dilution) for 24 h in the presence or absence of TGF-β1. Cell morphology of the mouse cardiac fibroblasts was analyzed by immunostaining for vimentin (red). Cell nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). (B) Transcriptome analysis for the gene expressions associated with ECM and ECM remodeling. Fold increase in the TGF-β1 and TGF-β1+ILC2-CM group represents fold change in gene expression of TGF-β1 vs Saline and TGF-β1+ILC2-CM vs TGF-β1 group, respectively. (C) mRNA expression of Postn and Tnc was analyzed by qRT-PCR. (D) qRT-PCR analysis on TGF-β1-induced Postn and Tnc in the presence or absence of BMP-7 neutralization antibody (1 μg/mL). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns, not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison post-hoc test. All values are means ± SD. Each dot indicates a biological replicate. (E) Working model for IL-33-mediated ILC2s expansion for protection against cardiac fibrosis. IL-33 treatment expands and activates cardiac ILC2s to secrete soluble factors including IL-13, IL-5, Areg, IL-10, G-CSF, and BMP-7. IL-13 is crucial for IL-33-mediated cardiac protective function by regulating M2 macrophage (M2ϕ) polarization. ILC2-derived BMP-7 alleviates TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation. Taken together, in combination with the increased M2 polarization, reduced ECM production, reduced CF activation, and reduced cell death within the myocardium, IL-33 alleviates cardiac fibrosis via the expansion of ILC2 and the effector functions of ILC2-derived paracrine factors.