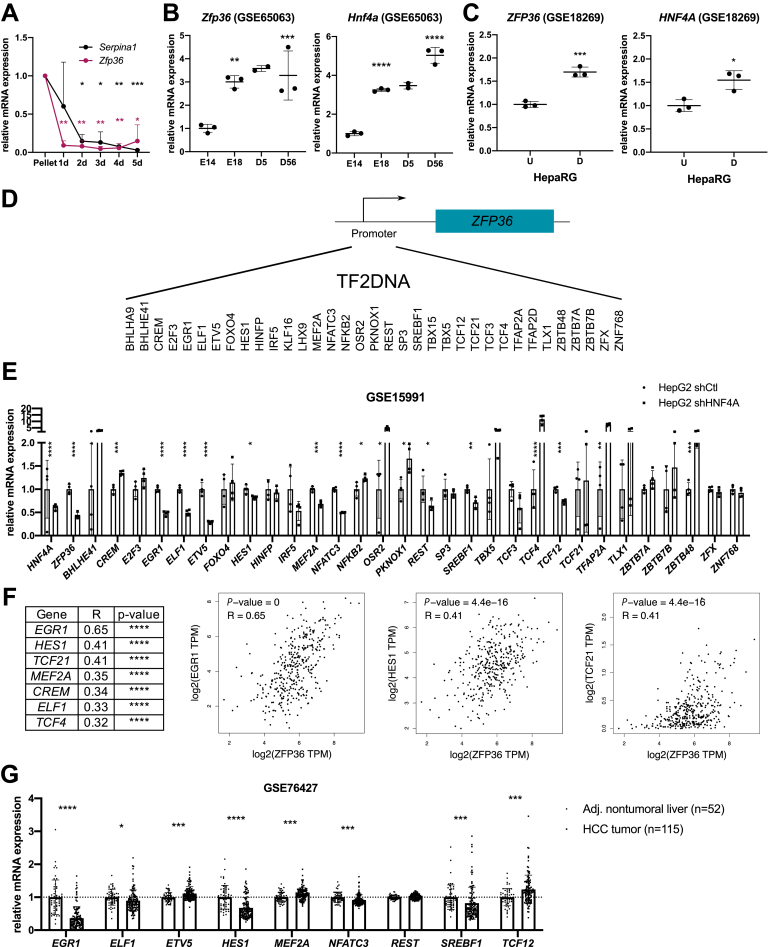
Figure 2.
TTP levels correlate with differentiation status of hepatocytes and expression of HNF4α/EGR1 in HCC. (A) Serpina1 (AAT) and Zfp36 (TTP) mRNA expression in isolated murine primary hepatocytes before (Pellet) and after plating during 5 days. Data represented as relative expression vs pellet and normalized by 18S gene. (B) Zfp36 and Hnf4a mRNA expression fold change during liver development (E, embryonic; D, days after birth) (GSE65063). (C) ZFP36 and HNF4A mRNA expression fold change in undifferentiated (U) vs differentiated (D) human HepaRG cell line (GSE18269). (D) Potential transcription factors binding to promoter of ZFP36 retrieved from TF2DNA. (E) Potential transcription factors mRNA expression in control (shCtl) and HNF4A knockdown by shRNA in HepG2 cells (shHNF4α) (GSE15991 transcriptomic data). Data represent mean ± standard deviation (SD). The t test for comparison with Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli correction for multiple comparisons (α = 5%) was used. (F) Correlation analysis between mRNA expression of ZFP36 and the best candidates predicted to act as transcription factors for ZFP36 in HCC (Pearson coefficient, LIHC TCGA cohort, GEPIA software). (G) mRNA fold change of potential transcription factors for TTP in non-tumoral liver (n = 52) and HCC tumors (n = 115) (GSE76427). Data represented as mean ± SD. The t test for comparison of 2 groups was used. P value was corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli procedure (α = 5%). ∗∗∗P < .001, ∗∗P < .01, ∗P < .05.