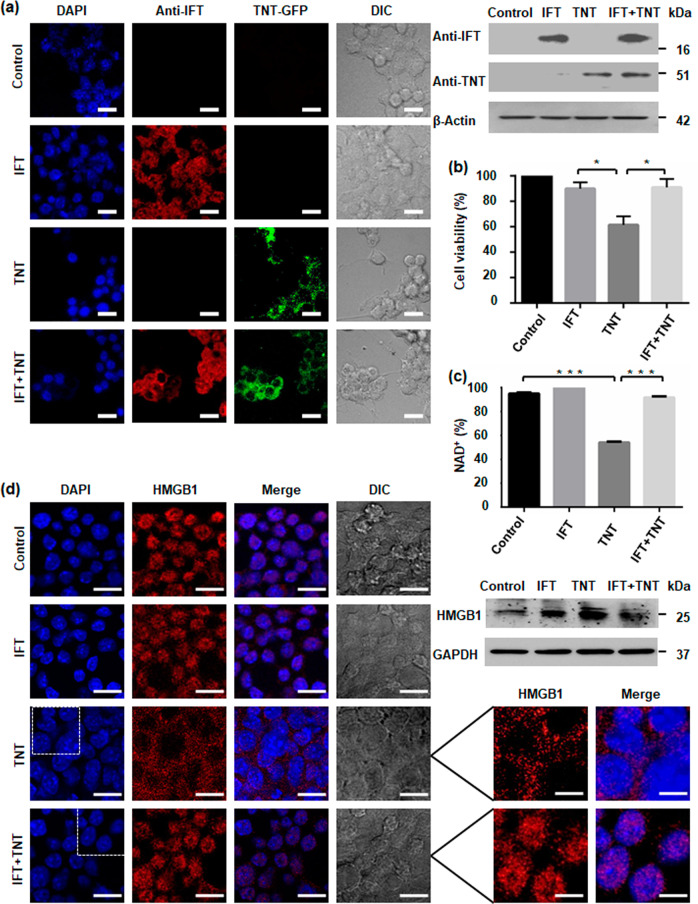
Fig. 2. Intracellular NAD+ levels regulate macrophage cell survival.
a Confocal microscopy images of RAW 264.7 cells expressing GFP-TNT or FLAG-IFT or both proteins after 48 h of post-transfection. Nucleus was visualized using DAPI (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). TNT expression was detected by GFP fluorescence and for IFT, cells were immunostained using anti-IFT antibody. Western blot analysis of transfected cells was performed with respective IFT or TNT antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Scale bar 25 μm, enlarged 10 μm. b MTT assay to determine cytotoxicity of TNT expression on transfected cells after 48 h of post-transfection. Cytotoxicity is measured as loss of viability. Increase in cell viability confirms that IFT inhibits TNT-mediated cell death. Cell viability of vector transfected sample was considered as 100%. Statistical significance was quantified using the unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, *p < 0.05. c Intracellular NAD+ content of transfected RAW 264.7 cells after 48 h of transfection; the relative percent NAD+ level was determined by enzyme-coupling assay. d Intracellular translocation of HMGB1 through confocal microscopy. Transfected murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells were stained with anti-HMGB1 antibody and DAPI. Inhibition of TNT-mediated cell death by IFT expression reduces cytosolic translocation of HMGB1 in co-transfected macrophages. Western blot analysis of HMGB1 was performed in culture supernatant of transfected cells. GAPDH is used as loading control. TNT expression induces HMGB1 translocation and extracellular release which is reverted by co-expression of IFT. Enlarged image showing HMGBI translocation. Scale bar 25 μm, enlarged 10 μm.