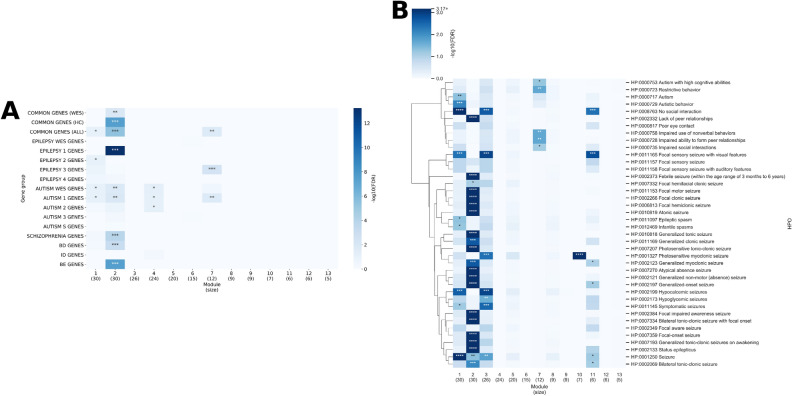
Figure 6.
Enrichment analysis on modules in the multiplex network generated with WES epilepsy and autism genes. The enrichment analysis of (A) different gene groups and (B) epilepsy and autism phenotypes over the 13 largest modules (those that have at least 5 genes) in the multiplex network generated using only WES epilepsy and autism genes. (A) The hypergeometric test was used to determine the p-value for enrichment in each gene group. The false discovery rate (FDR) is reported since multiple gene groups were tested. The background of the hypergeometric test is the 294 genes in the network. COMMON GENES (WES) = genes in both the epilepsy and autism WES gene lists, COMMON GENES (HC) = genes that are both in the epilepsy 1 subgroup and autism 1 subgroup (high confidence), COMMON GENES (ALL) = all genes in an epilepsy subgroup and autism subgroup, BD = bipolar disorder, ID = intellectual disability, BE GENES = genes that have a significantly higher expression in brain tissue vs control tissue. (B) The first cluster of HPO terms represent autism phenotypes and the rest represent epilepsy phenotypes. Only HPO IDs with gene-HPO relationships in the Phen2Gene knowledgebase are shown. The p-value was determined by computing the mean gene-phenotype association score for each HPO ID over the genes in the module and comparing it to the mean of 10,000 trials using n genes, where n is the size of the module, randomly chosen from the 294 genes in the WES multiplex network. The FDR is reported since multiple HPO IDs were tested. For both (A) and (B) “***” denotes FDR < 0.01, “**” denotes FDR < 0.05, and “*” denotes FDR < 0.1 and for (B) “****” denotes FDR < 0.0001. The heatmap and cluster map were generated using seaborn version 0.10.0 (https://seaborn.pydata.org/). The linkage on the rows of the cluster map was generated based on the distance between HPO IDs in the HPO tree.