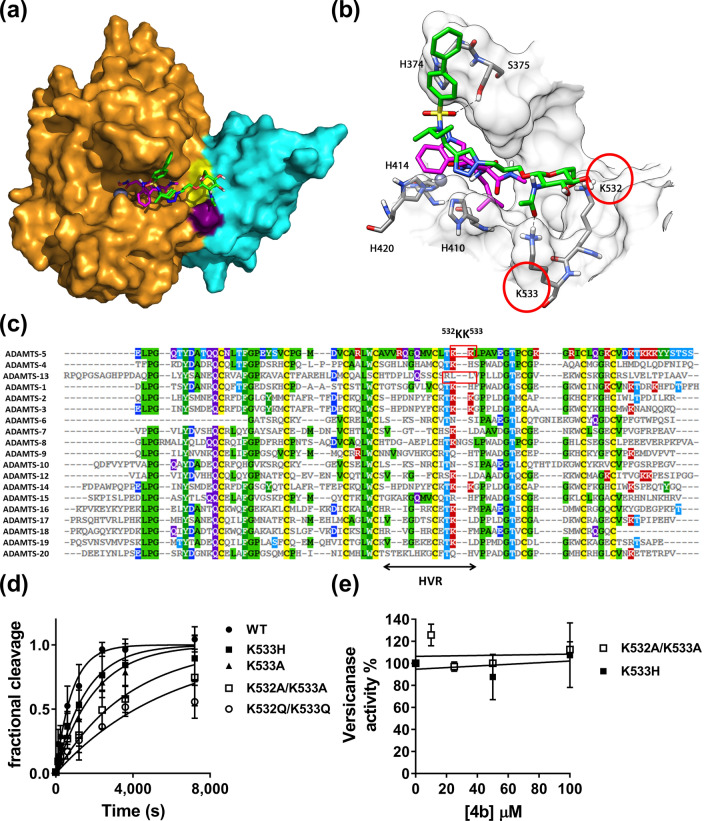
Figure 4.
Compound 4b binds to an exosite in the ADAMTS-5 Dis domain. (A, B) Minimized average structure of compound 4b bound to the ADAMTS-5-GM6001 complex, derived from the last 100 ns of MD simulation. (A) Protein surface. 4b is shown in green, GM6001 is in pink, ADAMTS-5 Mp domain in gold, the Dis domain in light blue, the active site zinc as a grey sphere. Exosite residues K532 and K533 are colored in yellow and purple, respectively. (B) Protein residues directly interacting with compound 4b. H-bonds are represented as black dashed lines. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of the Dis domain of all ADAMTS family members. Known exosites are boxed and the poorly conserved region (HVR, hypervariable region) is indicated. Conserved residues are indicated by the same color code. (D) Time course experiments for cleavage of 50 nM V1-5GAG by ADAMTS-5 MDTCS variants. Enzyme (0.4 nM) was incubated with 50 nM substrate. At the indicated time points, an aliquot was taken, stopped with EDTA and cleavage products measured by sandwich ELISA as described in the Methods section. The solid lines represent a nonlinear regression fit of the data. The data are presented as average ± SEM; n = 3–4. (E) Inhibition of ADAMTS-5 MDTCS variants by compound 4b. ADAMTS-5 K533H and K532A/K533A (0.82 nM) were incubated either with compound 4b or DMSO for 2 h at 37 °C before addition of V1-5GAG (50 nM). At each time point, reactions were stopped by addition of EDTA and cleavage fragments quantified by sandwich ELISA. The relative versicanase activity is presented and 100% activity corresponds to that in the presence of DMSO alone. The data are presented as average ± SEM; n = 3.