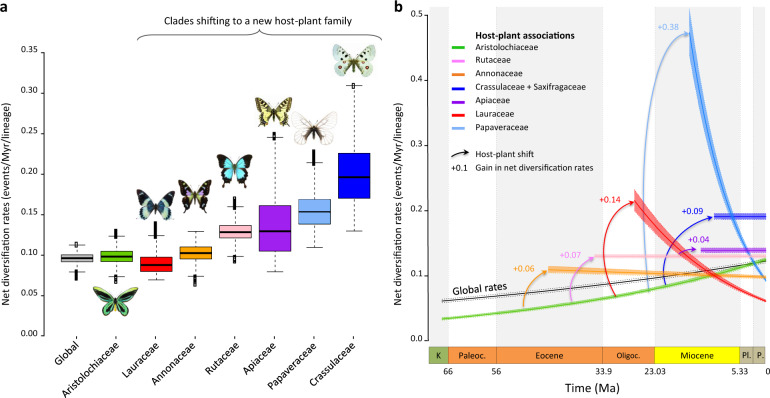
Fig. 3. Host–plant shifts lead to repeated bursts in diversification rates and a sustained overall increase in diversification through time.
a Diversification tends to be higher for clades shifting to new host plants, as estimated by trait-dependent diversification models. Boxplots represent Bayesian estimates of net diversification rates for clades feeding on particular host plants (see also Supplementary Fig. 12). b A global increase in diversification is recovered with birth–death models estimating time-dependent diversification (see also Supplementary Figs. 14 and 15). Taking into account rate heterogeneity by estimating host–plant and clade-specific diversification indicates positive gains of net diversification after shifting to new host plants (see also Supplementary Fig. 13). K Cretaceous, Paleoc. Paleocene, Oligoc. Oligocene, Pl Pliocene, P Pleistocene, Ma million years ago. Pictures of butterflies made by Fabien Condamine.