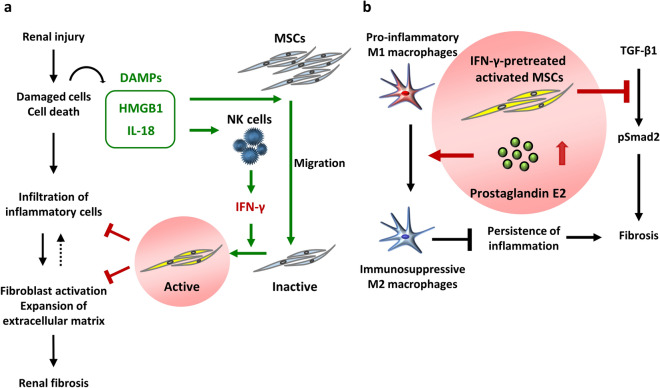
Figure 8.
DAMPs and the effects of MSCs treated with IFN-γ on renal fibrosis. (a) HMGB1 and IL-18 are members of DAMPs—HMGB1 was reported to promote the migration of MSCs, whereas IL-18 contributed to the secretion of IFN-γ. IFN-γ secreted from natural killer cells in injured tissues activates MSCs that exert anti-inflammatory effects. However, such activation require a long period of time, which delays the effect of MSCs administered for therapeutic purposes. (b) IFN-γ stimulation promotes the secretion of prostaglandin E2 from MSCs, and increased prostaglandin E2 induces polarization of immunosuppressive CD163-positive macrophages, suppressing the persistence of inflammation. MSCs treated with IFN-γ also directly inhibit profibrogenic TGF-β1/Smad signaling, leading to the prevention of fibrosis.