Figure 2.
Early epigenomic alterations in chromatin binding of Brd2,3, and 4 in response to RANKL & I-BET
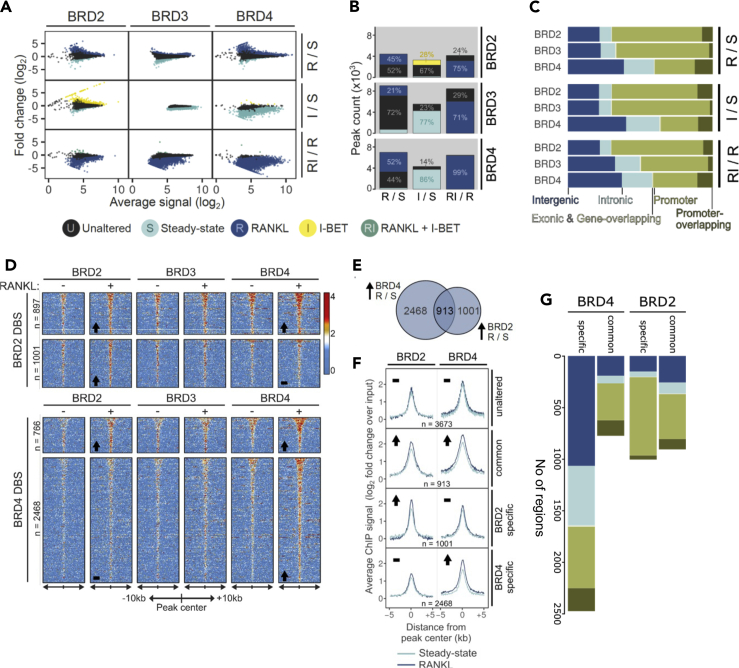
Differential binding of Brd2, Brd3, and Brd4 in response to RANKL (R), I-BET (I), or a combination of the two (RI) was analyzed 4 h after treatment. S: steady state
(A) Ratio-intensity plots of average ChIP signal and differential binding between conditions (log2 scale) are displayed for each BRD (columns) across treatment contrasts (rows).
(B) Number of differentially bound sites (DBSs) for BET proteins across pairwise treatment comparisons (from A). All DBS are colored by associated condition; non-significantly altered regions are colored gray.
(C) Genomic annotation for all DBS per condition.
(D) Relative enrichment of Brd2,3,4 on Brd2 (top) and Brd4 (bottom) DBSs. Fold change over input in a 20kb window around peak center was plotted for each BRD in S and R conditions, direction of change in Brd2/4 is indicated in lower left corner.
(E) Distribution of DBSs with increased Brd2, Brd4, or dual Brd2,4 enrichment upon RANKL induction.
(F) Average signal profiles for Brd2 and Brd4 across combined differential binding categories, direction of change in Brd2/4 is indicated in top left corner of each group.
(G) Genomic annotation of Brd2/4 binding locations relative to gene features in Brd2/Brd4 common or specific binding.