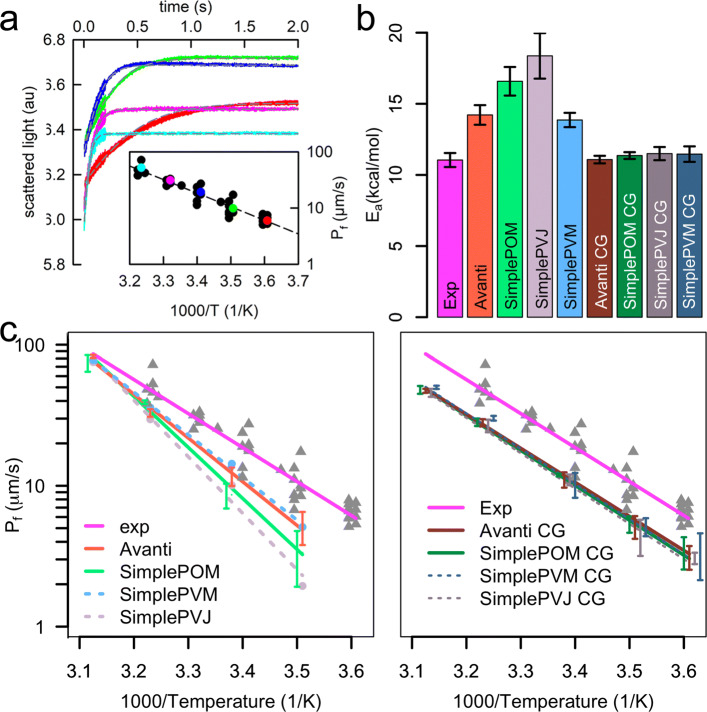
Fig. 4.
Water permeability over E. coli polar lipid extract membranes from in vitro experiment and in silico investigations. a Main figure: Representative scattering signals of E. coli PLE vesicles (in 100 mM NaCl, 20 mM MOPS at pH 7.40) subjected to an equal amount of hyperosmotic solution (100 mM NaCl, 20 mM MOPS, 150 mM sucrose, pH 7.40) in a stopped-flow apparatus at time zero. The fit of the analytical solution to the data is indicated as dashed gray lines. Different temperatures are color coded. Inset: Arrhenius plot of water flow through E. coli PLE membranes. A linear fit to the semilogarithmic plot revealed an E a of 11.05 ±0.49 kcal/mol. b E as of water permeation for all simulated systems and from in vitro experiment, the error bars denote the accuracy of the linear fit performed in c. c Comparison of water flux over different temperatures from atomistic membranes (left subfigure) and from CG membranes (right subfigure) to in vitro experiment