Fig. 2.
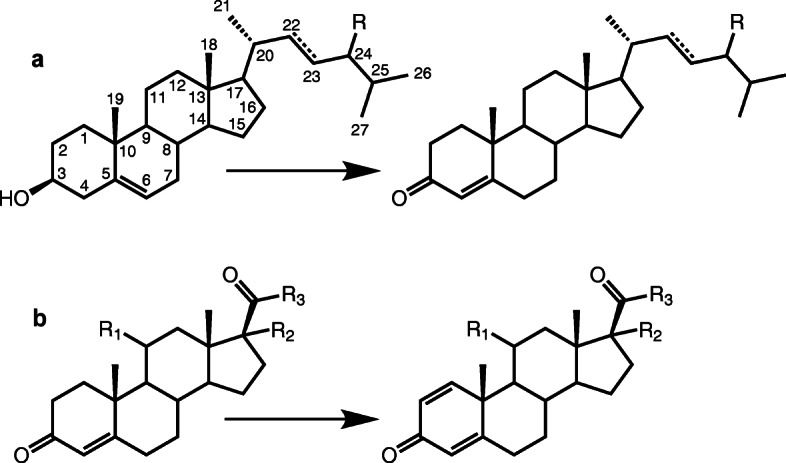
Major reactions of steroid bioconversion by N. simplex: a. Oxidation of 3-hydroxy group of phytosterol constituents: R = C2H5 β-sitosterol/stigmast-4-en-3-one (β-sitostenone); R = C2H5, Δ22,23stigmasterol/stigmasta-4,22-dien-3-one; R = CH3 campesterol/campest-4-en-3-one, R = CH3, brassicasterol/brassicast-4-en-3-one. b. R1 = H, R2 = H, R3 = CH3, Progesterone (Pr)/1(2)-dehydro-progesterone (DPr); R1 = H, R2 = OH, R3 = CH3, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OH-Pr)/1(2)-dehydro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OH-DPr); R1 = OH, R2 = OH, R3 = CH3, 11α,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone (11α,17α-di-OH-Pr)/1(2)-dehydro-11α,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone (11α,17α-di-OH-DPr); R1 = O, R2 = OH, R3 = CH2-O-C(O)-CH3 21-acetate of cortisone or cortisone acetate (AcC)/21-acetate of 1(2)-dehydro-cortisone or 21-acetate of prednisone (AcP)
