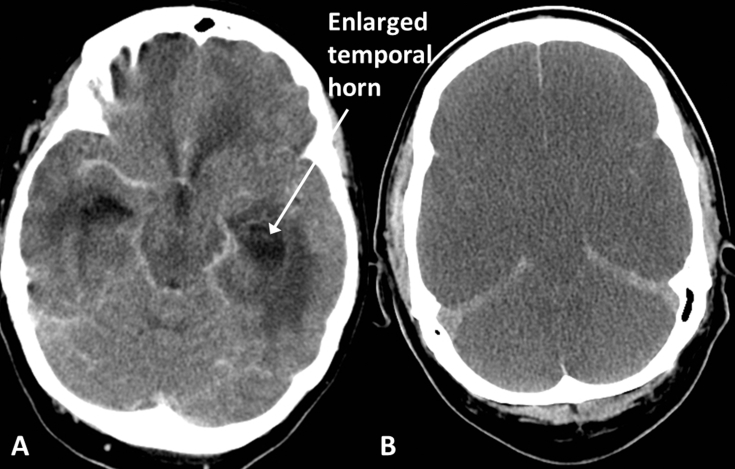
Fig 12.
(A) Hydrocephalus, in a patient with ventriculitis; note the enlarged temporal horns and surrounding low density oedema. (B) Diffuse hypoxic brain injury; note the diffuse loss of grey/white differentiation and generalised swelling causing effacement of the sulci and cisterns in this patient after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. There is no haemorrhage but the tentorium and falx appear dense relative to the adjacent hypodense oedematous brain.