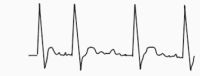
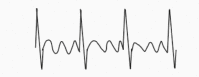
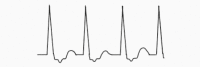
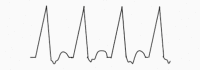
Table 6.
Classification of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Adapted from the Paediatric Critical Care Study Guide and the Advanced Paediatric Life Support treatment guidelines5,17,18
|
Unstable 1. Cardioversion
1. Vagal manoeuvre 2. Adenosine
|
||
|
|||
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
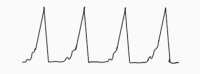 |
|
|
|
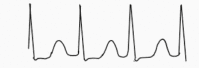 |
|
| |||
|
|
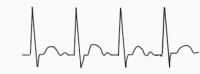 |
Treat underlying cause |
|
|
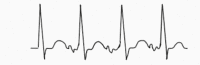 |
Slow automaticity
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
Kadam and colleagues.18
