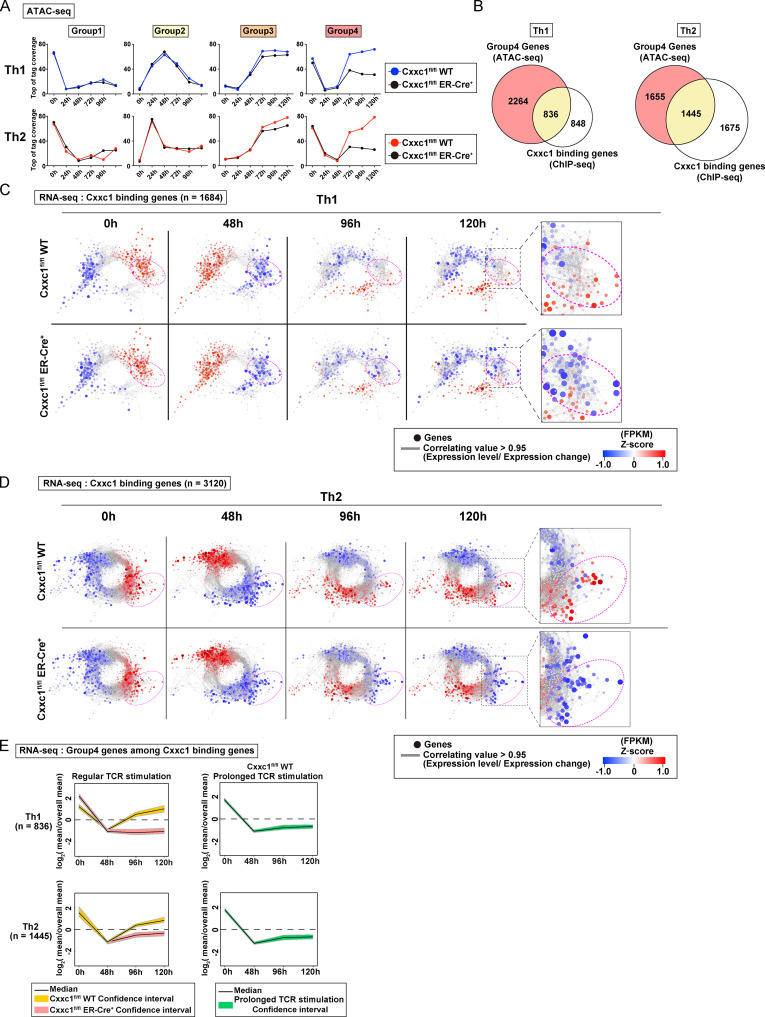
Figure 2.
Cxxc1 specifically regulates the expression of genes that are suppressed during the early phase and reactivated during the late phase. (A) The average tag count of each peak of ATAC-seq for differentiating Th1 or Th2 cells. Data from Cxxc1fl/fl WT or Cxxc1-deficient (Cxxc1fl/fl ER-Cre+) cells are shown for each group. WT data are adapted from Fig. 1 D. (B) The Venn diagrams display the overlap between the genes belonging to group 4 and Cxxc1-bound genes in Th1 and Th2 cells. (C and D) Coregulation transcriptome networks created based on two RNA-seq datasets (i.e., in naive [0 h] and the differentiation process [48 h] of WT cells) are shown. All Cxxc1-bound genes in Th1 (C; n = 1,684) and Th2 (D; n = 3,120) cells are shown. Dashed ellipsis (added manually) indicates genes down-regulated in the absence of Cxxc1. The node color indicates the gene expression levels at each time point (0, 48, 96, and 120 h) based on Z-scores. FPKM, fragments per kilobase of exon per million reads mapped. (E) A time-course analysis of the expression of Cxxc1-bound group 4 genes in WT, Cxxc1-deficient (left), and WT cells that received prolonged TCR/coreceptor stimulation (right). Lines denote the median, and shaded areas represent the 95% confidence intervals.