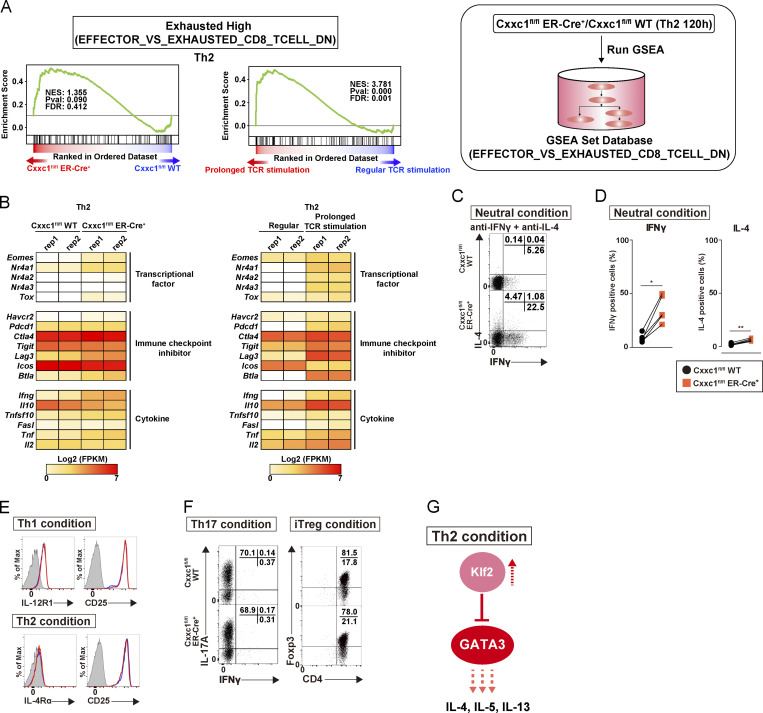
Figure S4.
Loss of Cxxc1 results in the enhanced expression of Th2 cytokines in CD4+ T cells (related to Fig. 4). (A) GSEA was performed as shown in Fig. 3 A. The genes were rank ordered based on relative expression in Cxxc1-deficient (red) versus WT (blue) Th2 cells (left) or prolonged (red) versus regular TCR/coreceptor stimulation (blue; right). (B) The heatmap shows the RNA expression of the genes that are reported to be dysregulated in exhausted CD8+ T cells. Genes encoding transcription factors, inhibitory receptors, and effector molecules were analyzed in WT versus Cxxc1-deficient (left) or regular versus prolonged TCR/coreceptor stimulation (right). FPKM, fragments per kilobase of exon per million reads mapped. (C and D) Naive CD4+ T cells from WT or Cxxc1-deficient mice were cultured under neutral conditions (in the presence of anti-IFNγ and anti-IL-4 Abs and IL-2). The cultured cells were restimulated with PMA plus ionomycin for 4 h. Intracellular staining profiles of IFNγ and IL-4 were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data from five independent experiments are shown (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (E) Cell surface staining of the indicated markers on CD4+ T cells from WT or Cxxc1-deficient mice cultured under Th1 (top) or Th2 (bottom) cell-inducing conditions. Staining with a control antibody is indicated by the gray shaded area. 20,000 events are displayed for each sample. (F) Naive CD4+ T cells from WT or Cxxc1-deficient mice were cultured under Th17 or iT reg cell–inducing conditions. The cultured Th17 cells were restimulated with PMA plus ionomycin for 4 h, and intracellular staining profiles of IFNγ and IL-17A were analyzed by flow cytometry (left). For iT reg cells, the Foxp3 expression was analyzed together with the CD4 expression by flow cytometry (right). Three independent experiments were performed with similar results. (G) A schematic representation of downstream signaling controlled by Cxxc1 in Th2 cells. Cxxc1 controls the Th2 cytokine expression via Klf2-dependent suppression of the GATA3. Thus, Cxxc1 deficiency results in the down-regulation of the Klf2 expression, hyperactivation of the GATA3, and hyperproduction of Th2 cytokines.