Figure 3.
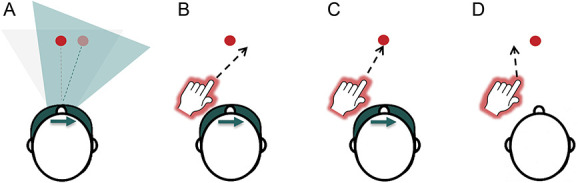
Prism adaptation procedure: In this example, a participant with left-CRPS is using rightward-shifting prisms (A–C), which induce adaptation towards the left (affected) side. For clarity of illustration, only one target (red circle) is represented in the figure. However, the treatment procedure involved 2 targets presented in the left and right side of space, and participants' pointing movements alternated between the left and right targets. (A) Prism goggles shift visual image to the right. The blue triangle represents a shift of visual perspective and perceived target location (pale red circle), relative to the real location of the target (light gray triangle, dark red circle). (B) Pointing movements initially err to the right. (C) Adaptive realignment results in correct pointing movements. (D) Goggles are removed and pointing movements err to the left (after-effect). CRPS, complex regional pain syndrome.
