Figure 3.
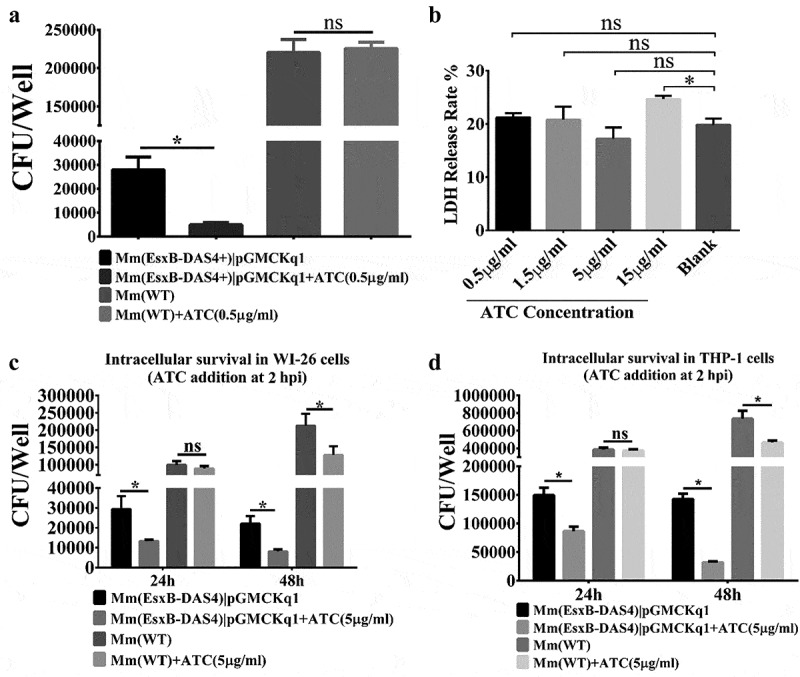
Inducible knockdown of EsxB reduced Mm intracellular survival. (a) Mm(EsxB-DAS4+)|pGMCKq1 and Mm(WT) were treated with/out ATC (0.5 μg/ml) for 48 h before single cell preparation. Then it was used to infect WI-26 cells at MOI = 2. At 48 hpi, the cells were collected and subjected to intracellular survival assay (CFU/well). The strains without ATC induction were used as controls. (b) WI-26 cells were treated with ATC at various concentrations for 48 h. The cytotoxicity was measured by LDH release assay. (c) WI-26 cells were infected with Mm(EsxB-DAS4+)|pGMCKq1 and Mm at MOI = 2. At 2 hpi, ATC (5 μg/ml) was added to the cell culture to induce degradation of EsxB-DAS4 +. At 24 and 48 hpi, the cells were harvested and subjected to intracellular survival assay (CFU/well). (d) Similarly, THP-1 cells were infected with Mm(EsxB-DAS4+)|pGMCKq1 or Mm at MOI = 1. At 2 hpi, ATC (5 μg/ml) was added to the cell culture to induce EsxB-DAS4+ degradation. At 24 and 48 hpi, the cells were harvested and subjected to intracellular survival assay (CFU/well). The cells without ATC addition were used as controls. The experiments were replicated for three times and the data is presented as mean ± SD. For cytotoxicity data, the statistical analysis was performed with One-way ANOVA, followed by Holm-Sidak multiple comparison. For CFU data, the statistical analysis was performed with multiple t test between ATC treated and nontreated groups of each strain. *< 0.05
