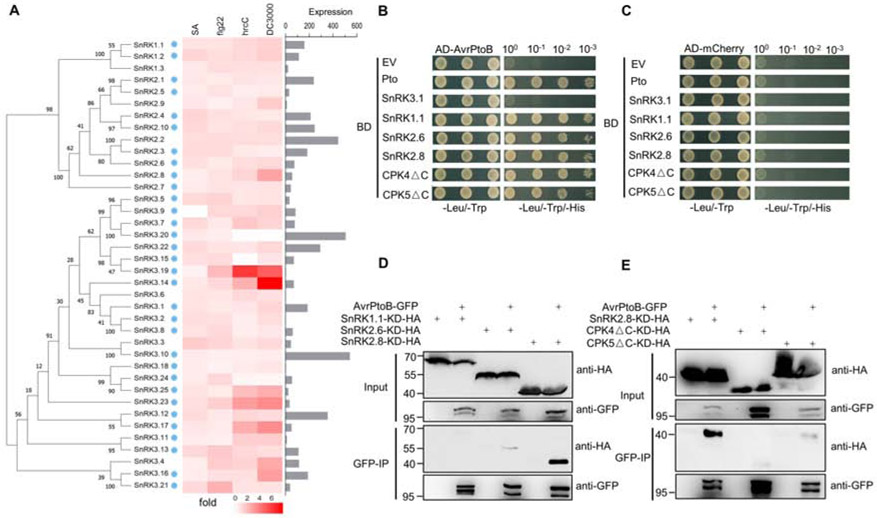
Figure 1. The Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPtoB interacts with the plant kinase SnRK2.8.
(A) Phylogeny of the Arabidopsis SnRK family and transcript expression of SnRK members after immune activation and pathogen infection. Phylogeny was determined by maximum likelihood method (1000 bootstrap replicates). The heat map shows fold change in leaf transcript expression one-hour post-treatment with SA, one hour post-treatment with flg22, and six hours post-infiltration with Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato strain hrcC. The bar graph represents the SnRK expression in leaf tissue. Data were obtained from BAR Expression Angler. Blue dots represent the SnRK members that were cloned for yeast-two hybrid. hrcC = P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hrcC mutant defective in Type III secretion system.
(B, C) Yeast two-hybrid assay of AvrPtoB and SnRK-CDPKs. AvrPtoB was co-expressed with Pto, SnRK3.1, SnRKl.1, SnRK2.6, SnRK2.8, as well as a C-terminal deletion of CPK4 (CPK4ΔC) and CPK5 (CPK5ΔC) in yeast. Empty vector (EV) and AD-mCherry were included as negative controls. Colony growth on SD -Leu/-Trp media confirms the presence of AD and BD vectors. Growth on SD -Leu/-Trp/-His media indicates protein-protein interaction. AD = activation domain vector, BD = binding domain vector.
(D, E) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of AvrPtoB-GFP with SnRK/CPKΔC kinase dead (KD)-HA variants in N. benthamiana. AvrPtoB-GFP under control of a dexamethasone (Dex)-inducible promoter was co-expressed with 35S::SnRKs-KD-HA and 35S::CPKsΔC-KD-HA in N. benthamiana using Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression. Expression of AvrPtoB-GFP was induced by 15 μM DEX for three hours at 24 hours post-infiltration. Protein extracts were subjected to anti-GFP immunoprecipitation (IP). The IP and input proteins were immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-GFP antibodies.