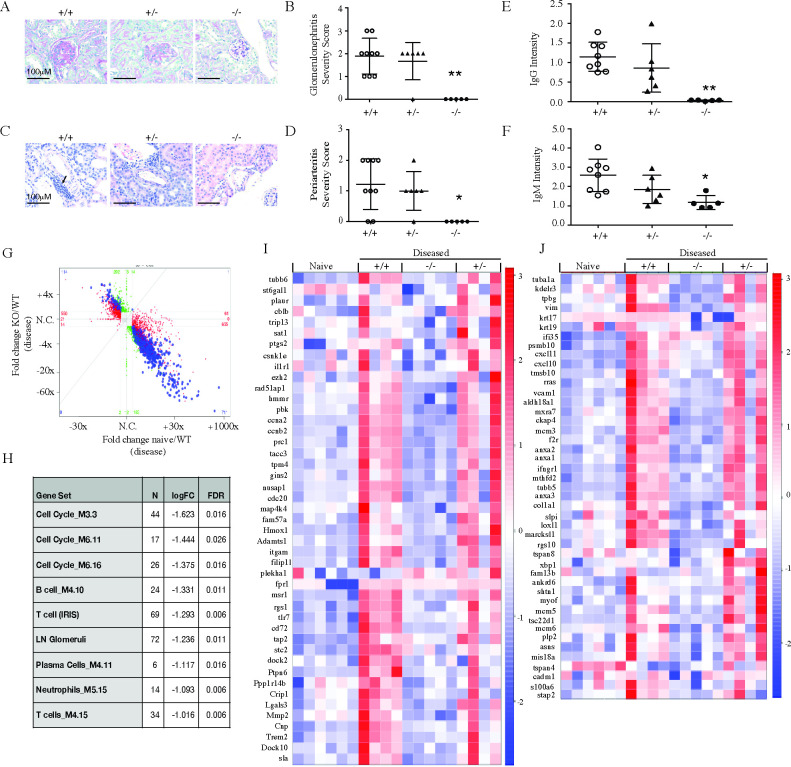
Fig 8. SLC15a4 deficient NZB/W F1 mice are protected from IFNα accelerated lupus nephritis.
7 weeks post rAd-IFNα administration, NZB/W F1 slc15a4+/+, slc15a4+/-and slc15a4-/- mice were euthanized and kidneys were collected to assess renal disease severity by histology and RNA sequencing. (A-D) Representative images and quantification of histological scoring for glomerulonephritis (A, B) and periarteritis (C, D) are shown. (E-F) Quantification of IgG (E) and IgM (F) immune complex deposition. Data is expressed as mean± SD. (G) RNA sequencing analysis was performed on kidney RNA. Fold changes between KO and WT at the disease timepoint are compared to those between naïve WT and disease WT animals. Each data point represents a gene. Red, green and blue dots represent genes that are significant only in naive versus diseased condition in wildtype (red), only in knockout versus diseased wildtype (green) or both (blue). (H) Gene set enrichment analysis of pre-defined immune and human LN ortholog gene modules are shown. (I-J) Effect of slc15a4 on human LN ortholog genes previously identified to be up-regulated in the glomerulus (I) or tubulointerstitium (J) of nephritic kidneys from human LN patients (see Material and Methods for details). Genes that showed individual significant changes in absence of slc15a4 are indicated (≥1.5 fold difference between groups with an adjusted p-value <0.01). Each column in the heatmap represents one animal within each group. *p < 0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005. N = 5–7 per group.