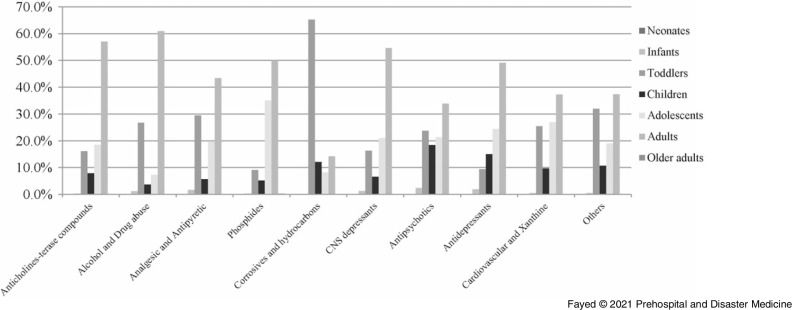
Figure 2.
Proportion of the Causative Agent Exposure According to the Age Groups Over the Period (March through May) of 2016-2020.
Abbreviation: CNS, Central Nervous System.
Anticholinesterase compounds exposure presented as follows: adults (57.0%), adolescents (18.6%), toddlers (16.2%), children (7.9%), and infants (0.3%).
Alcohols and drugs of abuse exposure presented as follows: adults (61.0%), toddlers (26.8%), adolescents (7.3%), children (3.7%), and infants (1.2%).
Analgesic antipyretic exposure presented as follows: adults (43.4%), toddlers (29.5%), adolescents (19.7%), children (5.7%), and infants (1.7%).
Phosphide exposure presented as follows: adults (50.0%), adolescents (35.1%), toddlers (9.1%), children (5.2%), infants (0.3%), and older adults (0.3%).
Corrosives and hydrocarbons exposure presented as follows: toddlers (65.3%), adults (14.3%), children (12.2%), and adolescents (8.2%).
CNS depressants exposure presented as follows: adults (54.6%), adolescents (21.1%), toddlers (16.4%), children (6.6%), and infants (1.3%).
Antipsychotics exposure presented as follows: adults (33.9%), toddlers (23.8%), adolescents (21.4%), children (18.5%), and infants (2.4%).
Antidepressants exposure presented as follows: adults (49.1%), adolescents (24.5%), children (15.1%), toddlers (9.4%), and infants (1.9%).
Cardiovascular and xanthine derivatives exposure presented as follows: adults (37.3%), adolescents (27.0%), toddlers (25.5%), children (9.7%), and infants (0.5%).
Other non-classified toxic exposure presented as follows: adults (37.4%), toddlers (32.0%), adolescents (19.0%), children (10.8%), and infants (0.5%).