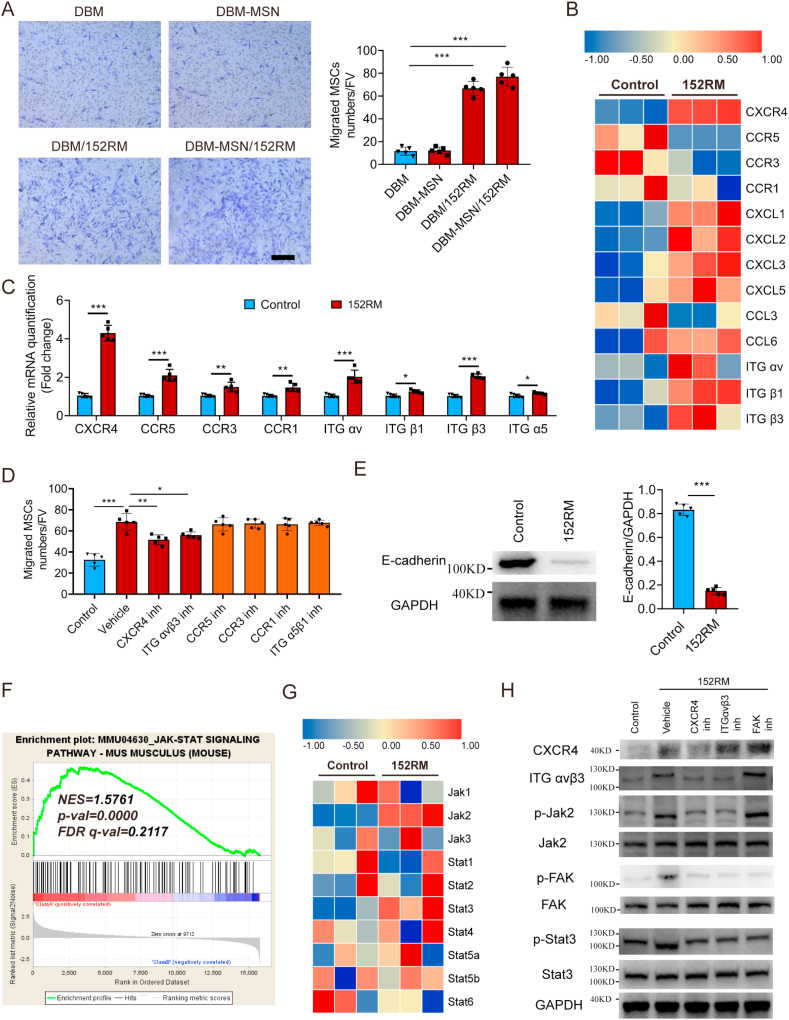
Fig. 3.
152RM induces the migration of MSCs partly through the FAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. (A) Transwell assays for the migration of MSCs using 152RM (n = 5 each). Representative crystal violet staining images are shown in the left panel. Quantification of cell migration is shown in the right panel. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) RNA-seq analysis showed the alteration of cell migration-specific gene expression in MSCs cultured with 152RM (n = 3 each). (C) Relative mRNA expression levels of cell migration-specific genes in MSCs cultured with 152RM (n = 5 each). (D) Quantification of the transwell assay and cell wound scratch assay after culture with 152RM, a CXCR4 inhibitor (AMD3100) and an Integrin αvβ3 inhibitor (Cyclo(-RGDfK)) (n = 5 each). (E) Western blot analysis of the expression of E-cadherin in MSCs after the addition of 152RM (n = 5 per group). (F) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) plots showing upregulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in MSCs cultured with 152RM (n = 3 each). (G) RNA-seq analysis showed alterations in JAK/STAT signaling pathway-related gene expression in MSCs cultured with 152RM (n = 3 each). (H) Western blot analysis of the expression of CXCR4, integrin αvβ3, p-Jak2, Jak2, p-FAK, FAK, p-STAT3 and STAT3 in MSCs (pretreated with a CXCR4 inhibitor (AMD3100) and an integrin αvβ3 inhibitor (cyclo(-RGDfK))) after the addition of 152RM (n = 5 per group). Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ANOVA and Student's t-test were employed. For all panels in this figure, data are representative of three independent experiments.