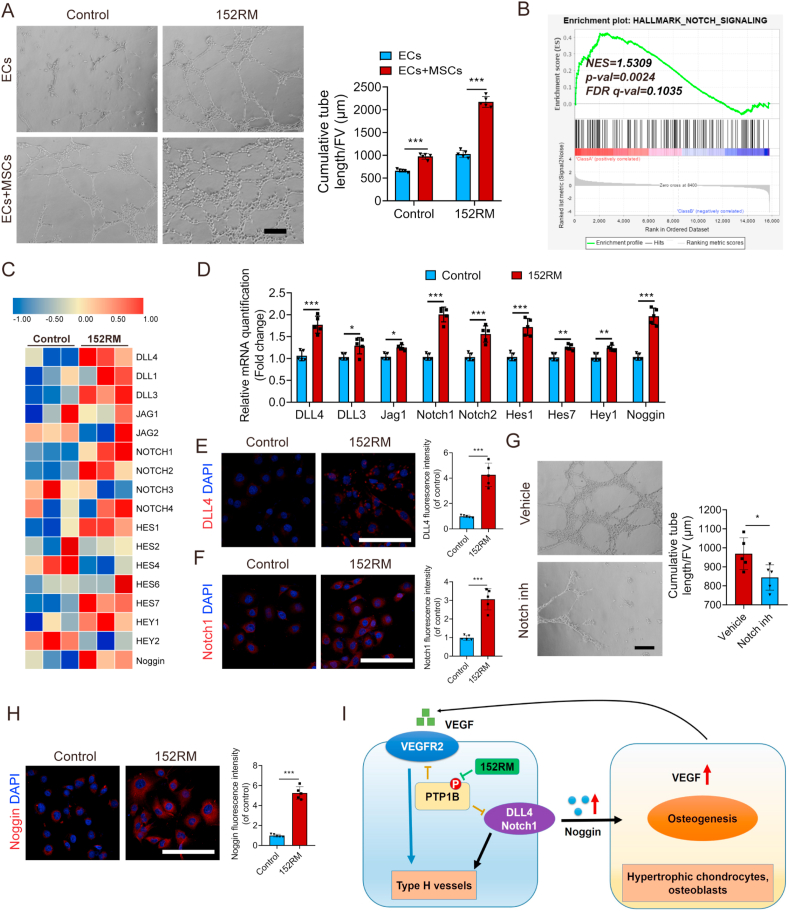
Fig. 6.
152RM promotes angiogenesis via the Notch signaling pathway. (A) Representative images of tube formation by ECs (with or without coculture with MSCs) after the addition of 152RM. Scale bar, 100 μm. The quantitative analysis of cumulative tube length is shown in the right panel (n = 5 per group). (B) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) plots showing upregulation of the Notch signaling pathway in ECs cultured with 152RM (n = 3 per group). (C) RNA-seq analysis showed alterations in Notch signaling pathway-related gene expression in ECs cultured with 152RM (n = 3 per group). (D) Relative mRNA expression levels of Notch signaling pathway-related genes in ECs cultured with 152RM (n = 5 each). (E) Representative immunostaining images of DLL4 (red) ECs with 152RM (n = 5 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Representative immunostaining images of Notch1 (red) ECs with 152RM (n = 5 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) Representative images of tube formation by ECs treated with 152RM (with or without Notch inhibitor). n = 5 per group. Scale bar, 100 μm. (H) Representative immunostaining images of Noggin (red) ECs with 152RM (n = 5 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (I) Schematic illustration of the role of 152RM in inducing the formation of type H vessels and coupling osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Student's t-test was employed. For all panels in this figure, data are representative of three independent experiments.