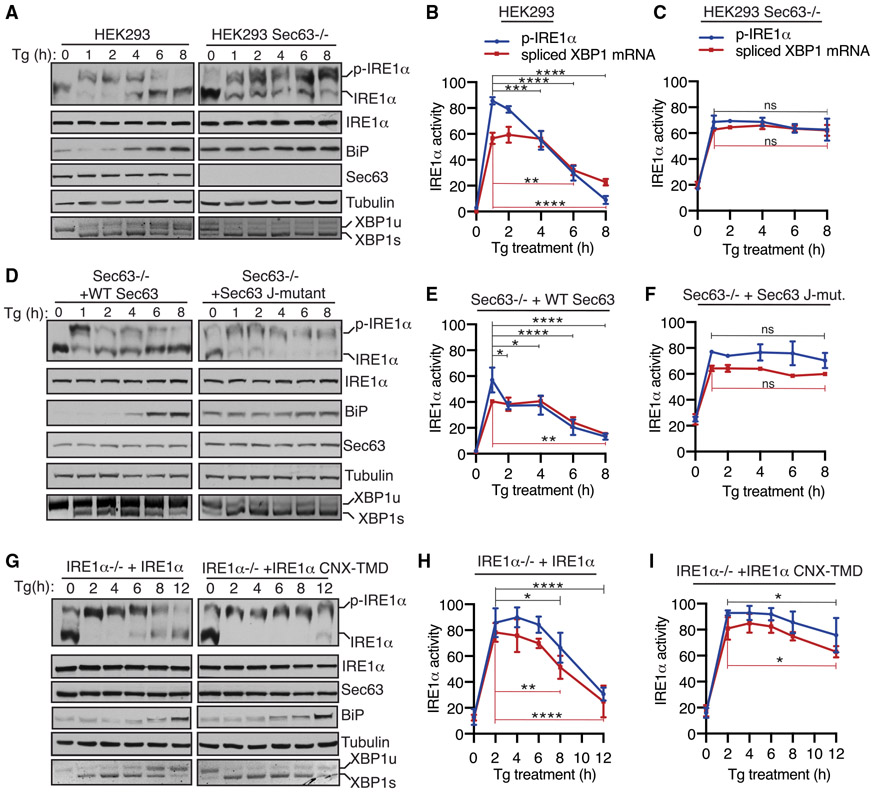
Figure 3. The J-Domain of Sec63 Is Essential for Attenuating IRE1α Activity during ER Stress in Cells.
(A) WT HEK293 or Sec63−/− cells were treated with 2.5 μg/mL Tg for the indicated time points and analyzed by immunoblotting. XBP1 mRNA splicing was assayed by RT-PCR. PCR products resulting from unspliced XBP1 (“XBP1u”) mRNA and spliced XBP1 (“XBP1s”) mRNA are indicated. p-IRE1α denotes the phosphorylated form of IRE1α, which migrates slower in Phos-tag immunoblotting.
(B and C) Quantification results of IRE1α phosphorylation and XBP1 mRNA splicing in (A). The percentage of IRE1α phosphorylation is calculated by dividing the signal for p-IRE1α by the sum of the signals for p-IRE1α and IRE1α. The percentage of XBP1s is calculated by dividing the signal for XBP1s by the sum of the signals for XBP1u and XBP1s. Statistical significance of IRE1α attenuation was compared between the 1-h time point (activated state) and later time points (2, 4, 6, and 8 h) using an ANOVA test. Error bars represent SEM. n = 3; ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
(D) Sec63−/− cells complemented with either WT or the J-domain mutant of Sec63 were treated and analyzed as in (A).
(E and F) Quantification results of IRE1α phosphorylation and XBP1 mRNA splicing in (D) were analyzed as in (B) and (C).
(G) HEK293 IRE1α−/− cells stably complemented with either WT IRE1α or IRE1α-CNX-TMD were treated with 2.5 μg/mL Tg for the indicated time points and analyzed as in (A).
(H and I) Quantification results of IRE1α phosphorylation and XBP1 mRNA splicing in (G) were analyzed as in (B) and (C).
Further data supporting these results are in Figure S8. See also Figures S2-S4.