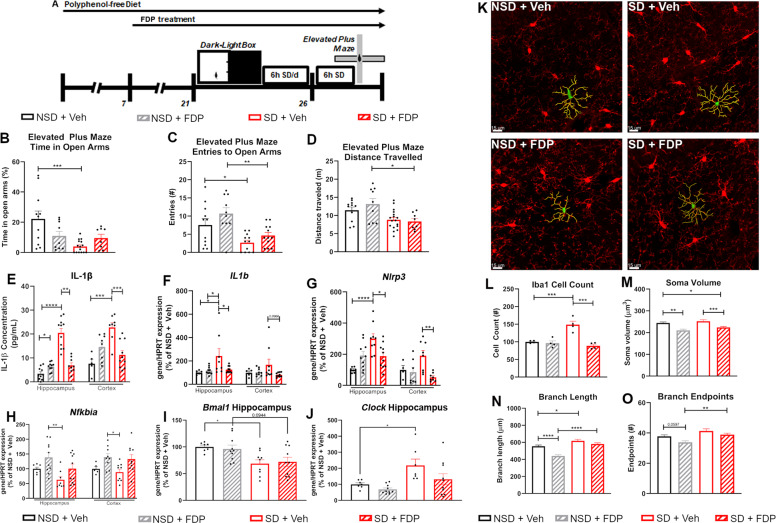
Fig. 1. Treatment with a polyphenol-rich diet attenuates SD-associated anxiety and neuroinflammation.
Analysis of behavior of wild-type mice treated with Vehicle or FDP, then tested in the Dark-Light Box task. Mice were then subjected to 6 hr SD for 6 days, then tested in the Elevated Plus Maze task. (A) Timeline of behavioral studies. (B) Percentage of Time spent in the Open Arms, (C) Entries into the Open Arms, and (D) Total Distance traveled during the Elevated Plus Maze task. N = 8–11 mice/group. (E) Production of IL-1β protein in the hippocampus and cortex. (F–J) mRNA expression of IL1b (F), Nlrp3 (G), Nfkbia (H), Bmal1 (I), and Clock (J) in the hippocampus and cortex. mRNA expression is compared to the expression of Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Hprt) and normalized to the mean of NSD + Veh mice. N = 7–10 mice/group for hippocampal samples, 5–10 for cortical samples. (K) Representative fluorescent images of CA1 hippocampal microglia. Red: Iba1. Green: Soma. Yellow: Branches. (L-O). Numbers (L), soma volume (M), total branch length per cell (N), and total branch endpoints per cell (O) of hippocampal microglia. N = 4 mice/group, >4 hippocampal sections studied per animal. For anatomical studies, >25 cells studied per section. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by Two-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test.