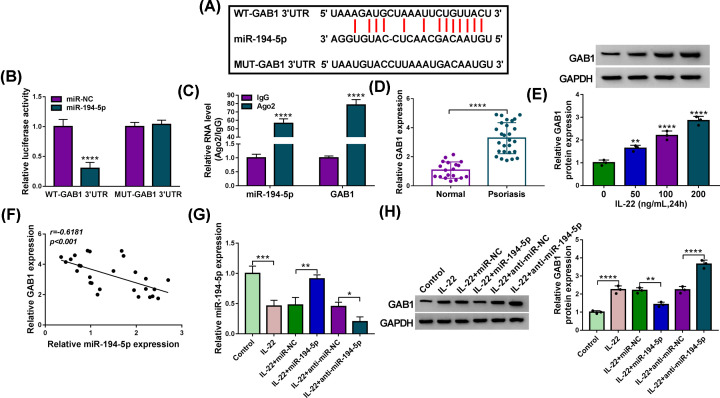
Figure 5. MiR-194-5p interacts with the 3′UTR of GAB1 in HaCaT cells.
(A) GAB1 was predicted to be a possible target of miR-194-5p via StarBase software, and their putative binding sequences were shown. The mutant miR-194-5p-binding sites in GAB1 were also shown. (B) The target interaction between miR-194-5p and GAB1 was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. HaCaT cells were co-transfected with luciferase plasmid (WT-GAB1 3′UTR or MUT-GAB1 3′UTR) and miR-194-5p or miR-NC for 48 h, and luciferase activities were examined. (C) RIP assay was carried out to confirm the interaction between miR-194-5p and GAB1. (D) The mRNA expression of GAB1 in 27 pairs of normal skin tissues and psoriasis lesional skin tissues was measured by qRT-PCR. (E) Western blot assay was performed to detect the protein level of GAB1 in HaCaT cells stimulated with 50, 100 or 200 ng/ml IL-22 for 24 h. (F) Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used to assess the linear correlation between the expression of miR-194-5p and GAB1. (G,H) The expression of miR-194-5p and GAB1 protein was examined in HaCaT cells in Control group, IL-22 group, IL-22 + miR-NC group, IL-22 + miR-194-5p group, IL-22 + anti-miR-NC group and IL-22 + anti-miR-194-5p group via qRT-PCR or Western blot assay, respectively. The experiments were independently repeated for three times with at least three technical repetitions. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.