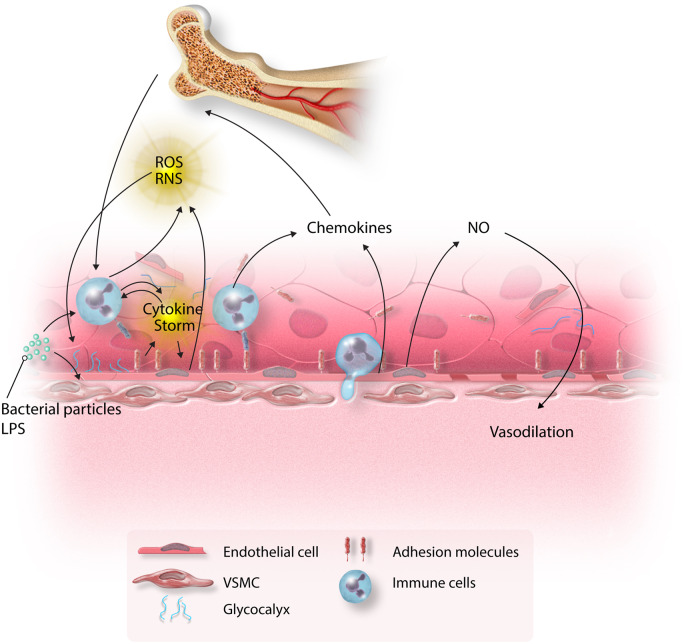
Figure 1.
Inflammatory cascade in sepsis. Bacterial components activate both immune cells and endothelium inducing cytokine production, which is self-perpetuating. Endothelial cells become activated and express adhesion molecules, to which immune cells bind. This initiates the process of transmigration of immune cells to the site of injury. ROS secreted by immune cells and endothelium further augment the inflammatory response. The combination of these insults leads to shedding of glycocalyx, induction of adhesion molecules, increased endothelial permeability, and endothelial apoptosis. Chemokines secreted by immune cells and endothelium recruit immune cells from the bone marrow. The shift in the eNOS/iNOS balance results in excess NO synthesis and vasodilation.