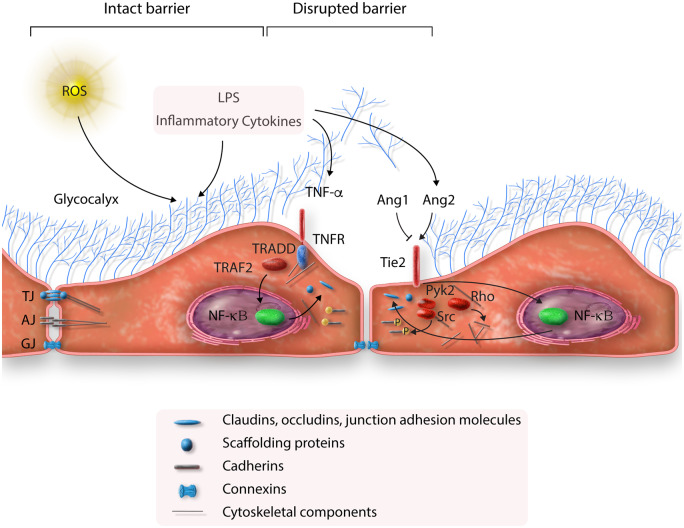
Figure 3.
Endothelial permeability in sepsis. ROS and bacterial components (i.e. LPS) damage the glycocalyx. LPS and inflammatory cytokines result in disruption of tight junctions (TJ), adherence junctions (AJ), and gap junctions (GJ) via activation of TNF-α and Ang2 pathways. The above effects increase endothelial permeability (see text for details).