Fig. 4. Construct of injectable SrCO3/HSA composite hydrogels (HSA).
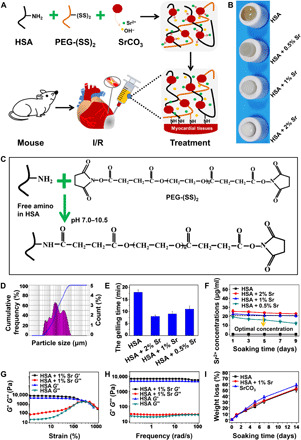
(A) Design schematic of SrCO3/HSA composite hydrogels for injection into I/R mice. (B) The pictures of SrCO3/HSA composite hydrogels with different SrCO3 contents. (C) The gelation mechanism and chemical reactions between HSA and PEG-(SS)2. (D) The particle size distribution of the SrCO3 powder. (E) Gelling time of SrCO3/HSA composite hydrogels. (F) Concentrations of Sr ions released from hydrogels. Experiments were conducted in triplicate. (G) Elastic moduli (G′) and viscous moduli (G″) as a function of the strain of HSA hydrogel and HSA + 1% Sr composite hydrogel. (H) G′ and G″ as a function of the frequency of HSA hydrogel and HSA + 1% Sr composite hydrogel. (I) The weight loss of the HSA hydrogel, HSA + 1% Sr composite hydrogel, and SrCO3 powders inside the HSA + 1% Sr composite hydrogel after soaking in tris-HCl buffer solution (pH 7.4) at different time points. Experiments were conducted in triplicate. All data are presented as means ± SEM. (Photo credit: Min Xing, State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, P. R. China.)
