Fig. 3. BIR domains pull down proteins with free Nt-α-amino groups after NatA RNAi.
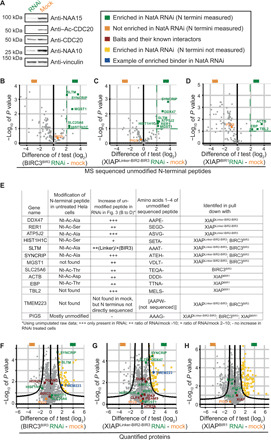
(A) Left: Immunoblots (IBs) for NAA10, NAA15 (NatA subunits), Ac-CDC20, CDC20, and vinculin for RNAi-treated and mock-treated cells after 48 hours. “Mock” here and elsewhere means transfection without small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Lysates were used for pull-downs in (B to D) and (F to H). Right: Legend of color coding for (B to D) and (F to H). (B to D) His-tag BIR domains BIRC3BIR3, XIAPLinker-BIR2-BIR3, and XIAPBIR1 were used to pull down proteins from HeLa lysates treated with RNAi for NatA or mock and 3 hours with MG132 before harvesting. Volcano plots for the quantified free Nt-α-amino peptides for BIRC3BIR3 (B), XIAPLinker-BIR2-BIR3 (C), and XIAPBIR1 (D) are shown. Peptides enriched significantly in the NatA RNAi–treated samples are displayed in green (t test: P < 0.1, t test difference > 2); a control peptide from PIGS already known to be usually in the free Nt-α-amino form is colored in orange. (E) Table of proteins whose unmodified N-terminal peptides were specifically enriched in samples treated with RNAi for NatA [shown in (B to D)]. TMEM223, an example of a specific binder from the protein volcano plots [shown in (F and G)], and PIGS as nonspecific binder are also shown. Reported in the table are gene name, state of modification of the N-terminal peptide under unperturbed conditions (from N-terminome data; table S1), extent of enrichment of the unmodified N-terminal peptide in RNAi versus mock experiments extracted from the measured MS raw data, sequence of residues 1 to 4 of the N-terminal peptide measured in MS, and the bait used for the pull-down. (F to H) Volcano plots showing all quantified proteins (not limited to those whose N termini were directly sequenced) from the same pull-down experiments described in (B to D). Cutoff values: FDR < 0.05 and S0 > 1.
