Fig. 3. Structures of the electrode and 3D printing coaxial FASC device.
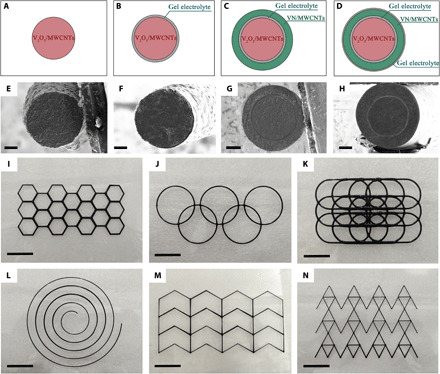
(A to D) Schematic illustrations of the cross-sectional view of the V2O5 NW/MWCNT fiber, V2O5 NWs/MWCNTs@gel electrolyte fiber, V2O5 NWs/MWCNTs@gel electrolyte@VN NW/MWCNT fiber, and the 3D printing coaxial FASC device struts. The cross-sectional SEM images of (E) V2O5 NW/MWCNT fiber, (F) V2O5 NWs/MWCNTs@gel electrolyte fiber, (G) V2O5 NWs/MWCNTs@gel electrolyte@VN NW/MWCNT fiber, and (H) the 3D printing coaxial FASC device by DCMW. (I to N) The printed FASC device with different patterns. Scale bars, 50 μm (E and F), 100 μm (G and H), and 10 mm (I to N). Photo credit: (I to N) Hongyu Lu, Xi’an University of Technology.
