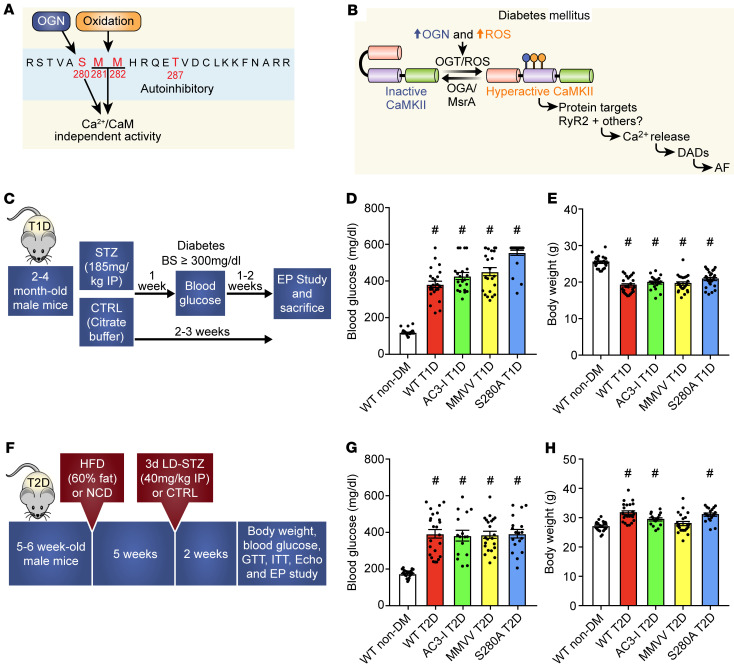
Figure 1. Proposed CaMKII posttranslational modifications and type 1 and type 2 diabetic models.
(A) Oxidation at methionines 281/282 and OGN at serine 280 are posttranslational modifications hypothesized to promote diabetic heart disease and arrhythmias. (B) Schematic representation of proposed hypothesis that excessive ROS and OGN in diabetes mellitus (DM) promotes AF through CaMKII-dependent signaling. (C) Schematic of diabetes induction and experimental protocol for T1D. Summary data for (D) blood glucose and (E) body weight in nondiabetic and T1D mice 2 weeks after STZ injection. (F) Schematic of DM induction and experimental protocol for T2D. Summary data for (G) blood glucose and (H) body weight in nondiabetic and T2D mice 2 weeks after LD-STZ injection. T1D, type 1 DM; T2D, type 2 DM; HFD, high-fat diet; LD-STZ, low-dose STZ; NCD, normal chow diet; OGN, O-GlcNAcylation; RyR2, ryanodine receptor type 2; STZ, streptozocin. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (D, E, G, and H) (#P < 0.0001 vs. WT non-DM, *P < 0.05 vs. WT non-DM).