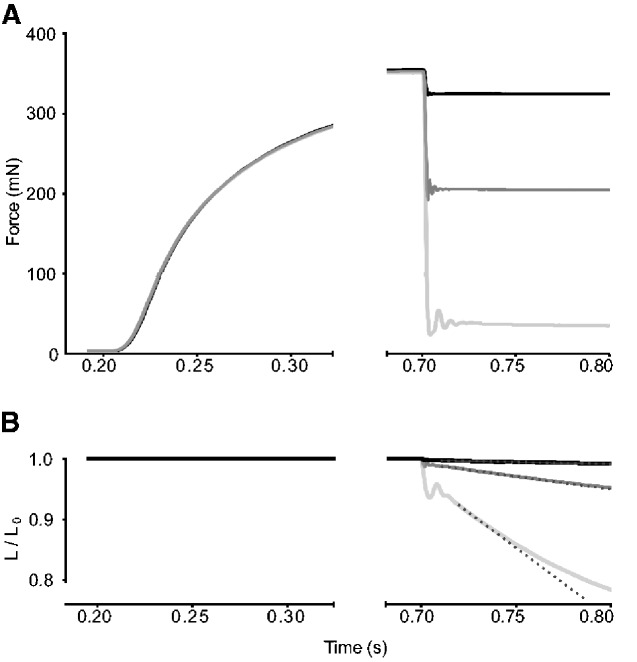
Fig. 3.
Example force-hold contractions of a BB muscle bundle in Nile crocodile. (A) After 200 ms, the stimulus was initiated, and the maximum isometric force was reached after 650 ms. In this example, three separate force time-courses are overlaid; force-rise was the same in each record. In the middle (dark grey) record, the targeted submaximal force was pre-set at 200 mN. A step-change of muscle length allowed the system to rapidly achieve the 200 mN target, and thereafter the stable length-change needed to hold the force stable was recorded. (B) Stable rates of muscle shortening (dotted lines) were determined with force clamped at different levels. Length-change was stable for 10 to 30 ms; the shortest linear periods were associated with the fastest shortening speeds attained (light grey). For clarity, the time-courses after the stimulus was stopped (at 800 ms) are not shown because the system was still holding force stable for a short period while the muscle relaxed.