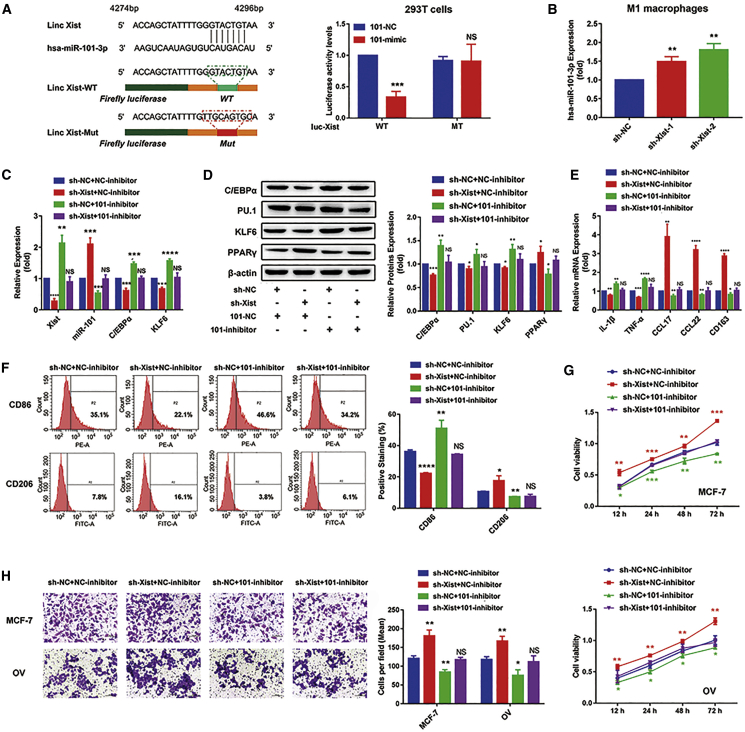
Figure 6.
The Xist/miR-101/C/EBPα/KLF6 axis mediates macrophage polarization to regulate tumor cell proliferation and migration
(A) The sequence of Xist with a highly conserved putative miR-101-binding site from the starBase 2.0 prediction and the luciferase activity of the 293T cells cotransfected with the miR-101-mimic or NC-mimic and containing WT/ MT-Xist by dual luciferase reporter assays. (B) The relative expression of miR-101 in the M1 macrophages after silencing Xist by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. (C−F) sh-NC + NC-inhibitor, sh-Xist + NC-inhibitor, sh-NC + 101-inhibitor, and sh-Xist + 101-inhibitor were, respectively, transfected in M1 macrophages. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR results showing the relative mRNA expression of Xist, miR-101, C/EBPα, and KLF6. (D) Western blot results showing the protein expression of C/EBPα, KLF6, PU.1, and PPARγ. (E) Quantitative real-time PCR results showing the relative mRNA expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, CCL17, CCL22, and CD163. (F) Flow cytometry results showing the surface expression of CD86 and CD206. (G and H) MCF-7 and OV cells were cocultured with M1 conditional medium transfected with sh-NC + NC-inhibitor, sh-Xist + NC-inhibitor, sh-NC + 101-inhibitor, and sh-Xist + 101-inhibitor. (G) MTT results showing the proliferation abilities of MCF-7 and OV cells. Transwell results showing the migration abilities of MCF-7 and OV cells (H). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n = 3; mean ± SD.