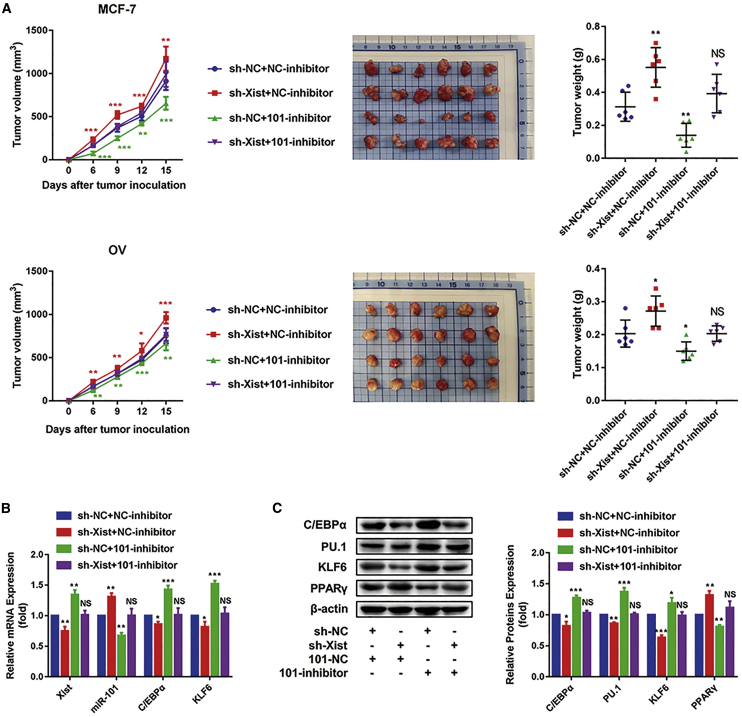
Figure 7.
The Xist/miR-101-3p/KLF6/C/EBPα axis mediates macrophage polarization to promote breast and ovarian cancer development
MCF-7 and macrophage with sh-NC + NC-inhibitor, MCF-7 and macrophage with sh-Xist + NC-inhibitor, MCF-7 and macrophage with sh-NC + 101-inhibitor, MCF-7 and macrophage with sh-Xist + 101-inhibitor, OV and macrophage with sh-NC + NC-inhibitor, OV and macrophage with sh-Xist + NC-inhibitor, OV and macrophage with sh-NC + 101-inhibitor, and OV and macrophage with sh-Xist + 101-inhibitor were inoculated into mice to construct subcutaneous tumors, respectively (n = 6 mice in each group). After inoculation, the macrophage with sh-NC + NC-inhibitor, macrophage with sh-Xist + NC-inhibitor, macrophage with sh-NC + 101-inhibitor, and macrophage with sh-Xist + 101-inhibitor were injected into tissues one time/3 days until the mice were killed; the volumes of tumors were measured every 3 days. (A) Tumor size, tumor weight, and tumor volumes after treatment. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR results showing the relative mRNA expression of Xist, miR-101, C/EBPα, and KLF6. (C) Western blot results showing the protein expression of C/EBPα, KLF6, PU.1, and PPARγ. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n = 3; mean ± SD.