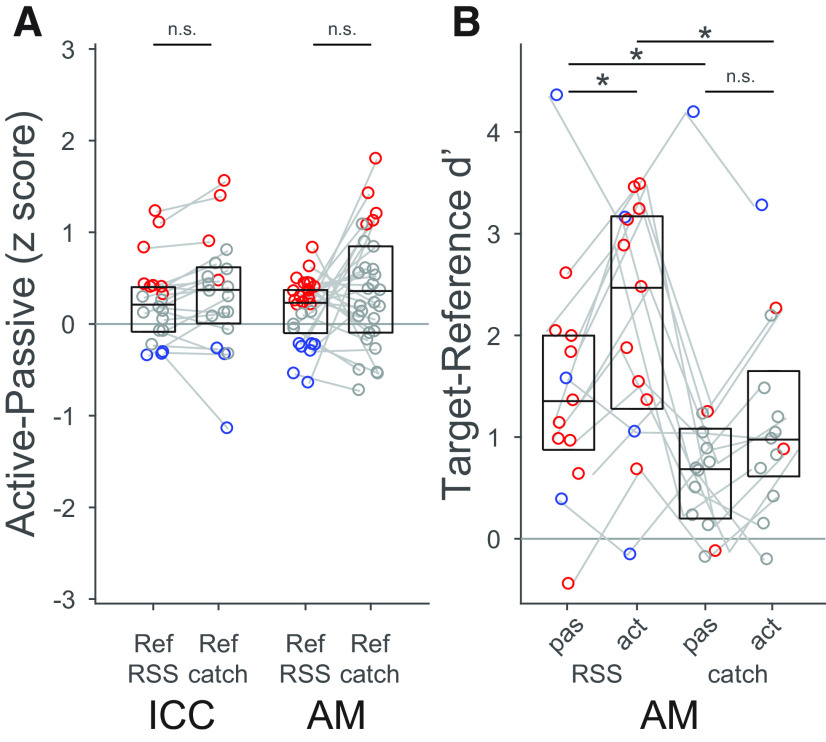
Figure 5.
Neural discriminability between targets and catch references was lower than between targets and noncatch references. A, Change in z-scored response to RSS and 1/f spectrum catch references between active and passive conditions (n = 20 ICC, n = 29 AM neurons with significant engagement effects on reference or target responses and presented at least 2 catch stimuli per behavior condition). B, Target-versus-RSS reference d′, and target versus catch d′ in passive and active states (n = 29 AM neurons with significant engagement effects on target-vs-reference d′ and with at least 2 catch stimuli). Exclusion criteria eliminated all but 2 ICC neurons, so only AM data are shown. A, B, Red represents a significant rate increase during task engagement. Blue represents a significant decrease. Boxes represent median and interquartile range. *Pairs of conditions with a significant median difference (p < 0.05, signed-rank test). n.s. Not significant.