Fig. 3.
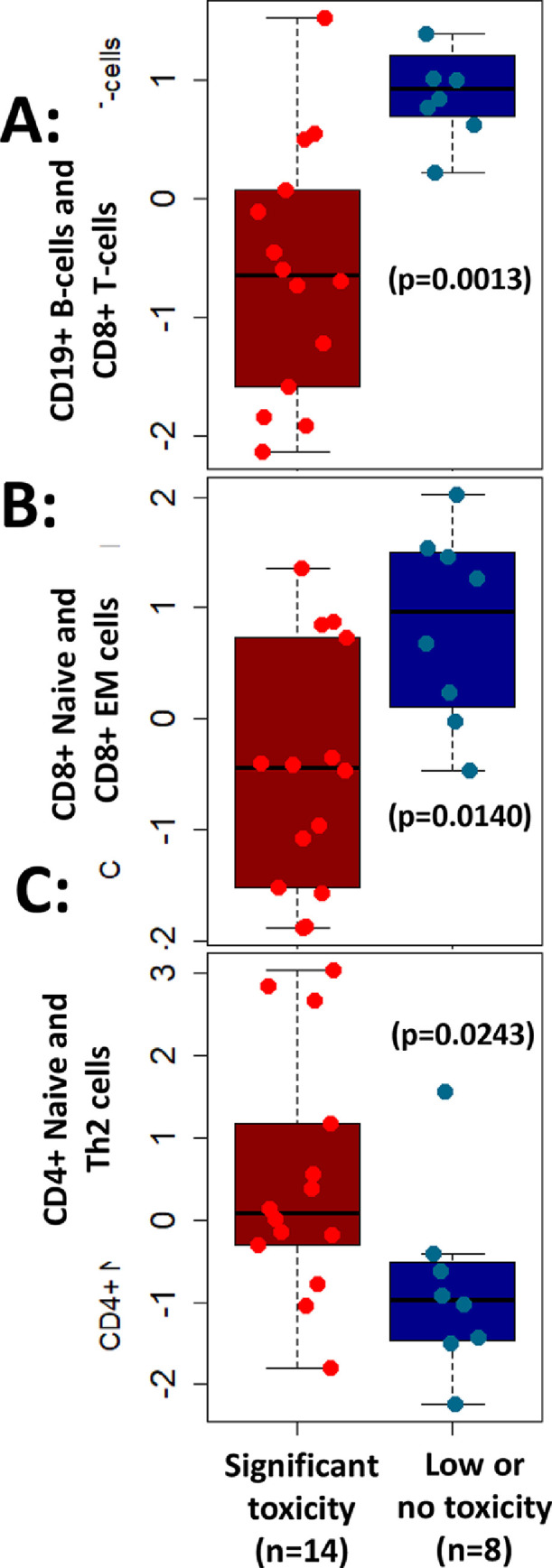
Association of peripheral immune cells with clinical toxicity. Multi-marker assessments revealed higher levels of (A) CD19+ B-cells and CD8+ T-cells (p = 0.0013) or (B) phenotypically naive CD8+ and effector memory (EM) CD8+ T-cells (p = 0.0140) associated with lower or no toxicity in patients. In addition, (C) lower levels of CD4+ naive and Th2 cells were associated with lower or no toxicity (p = 0.0243) and vice versa.
