FIGURE 4.
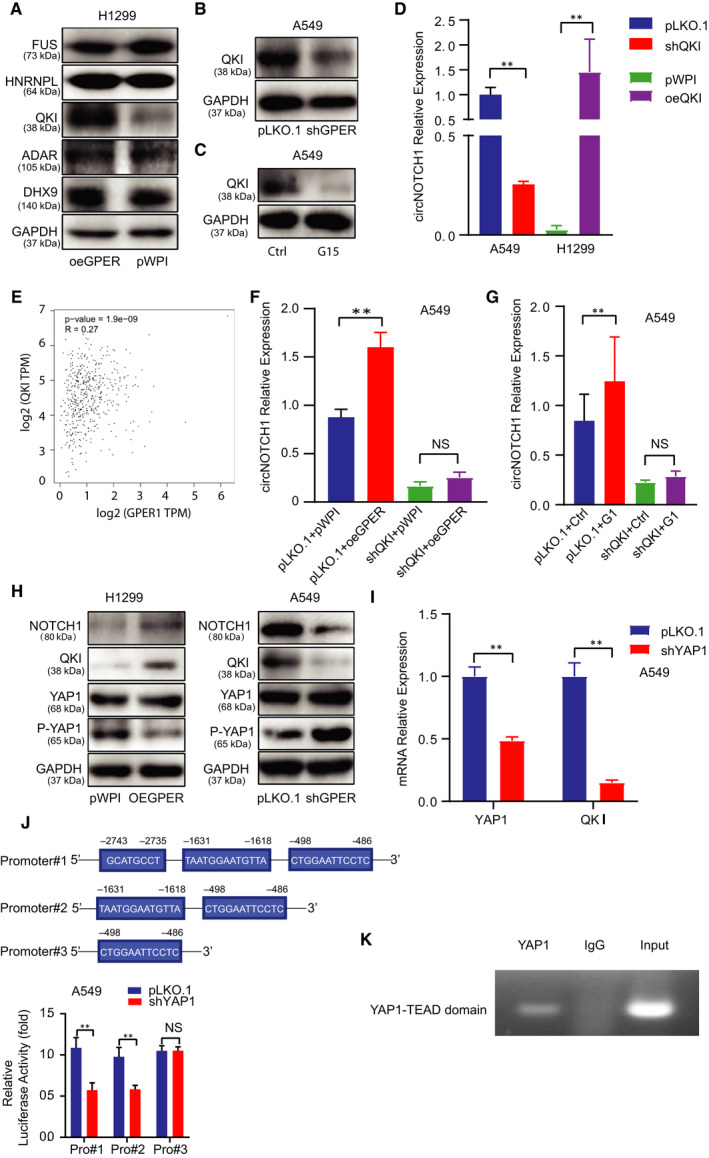
GPER regulated circNOTCH1 expression: via transcriptional regulation on QKI by YAP1/TEAD complex. (A) Western blot assay was conducted to screen a panel of transacting RNA‐binding factors in H1299 cells transfected with oeGPER or pWPI vector (right). (B) Western blot assay was performed to detect QKI expression in A549 cells w/wo shGPER. (C) Western blot assay was conducted to detect QKI expression in A549 cells treated with G15. (D) qRT‐PCR assay was conducted to detect circNOTCH1 expression in A549 cells transfected with pLKO.1 or shQKI (left) and in H1299 cells transfected with pWPI or oeQKI (right). (E) Correlation between GPER and QKI was analysed from the TCGA data. (F) qRT‐PCR assay was conducted to test circNOTCH1 expression using A549 cells transfected as indicated: pLKO.1 + pWPI, pLKO.1 + oeGPER, shQKI + pWPI, shQKI + oeGPER. (G) qRT‐PCR assay was conducted to test circNOTCH1 expression using A549 cells transfected with pLKO.1 or shQKI and subsequently treated with mock or G1. (H) Western blot assay was performed to examine NOTCH1, QKI, YAP1 and P‐YAP1 levels in H1299 cells transfected with pWPI vector or oeGPER (left) and in A549 cells transfected with pLKO.1 vector or shGPER (right). (I) qRT‐PCR assay was conducted to show the efficiency of YAP1 knock‐down and QKI mRNA expression. (J) The luciferase assay was performed to examine three YAP1‐TEAD elements viability in A549 cells transfected w/wo shYAP1. (K) ChIP assay was conducted to confirm the second TEAD element of QKI could bind with the YAP1. Quantitation was presented as mean ± SD, and P values were calculated by t test, **P < .01
