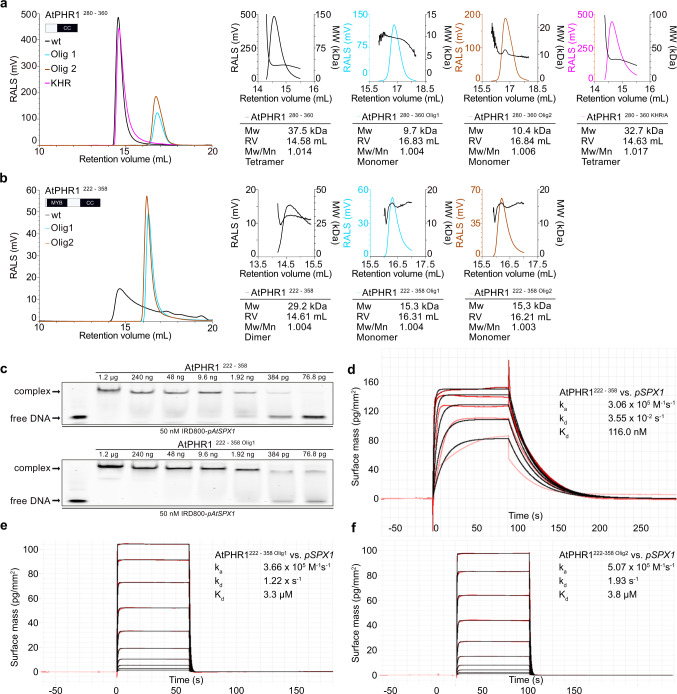
Fig. 2. Mutations in the AtPHR1 coiled-coil domain impair oligomerisation and DNA binding.
a Analytical size-exclusion chromatography traces of wild-type AtPHR1 CC (wt, black line), AtPHR1280–360 Olig1 (Olig1, cyan), AtPHR1280–360 Olig2 (Olig2, orange), and of AtPHR1280–360 KHR/A (KHR, magenta). The corresponding right-angle light scattering (RALS) traces are shown alongside, the molecular masses are depicted by a black line. Table summaries provide the molecular weight (Mw), retention volume (RV), dispersity (Mw/Mn), and the derived oligomeric state of the respective sample. b Analysis of AtPHR1 MYB-CC (AtPHR1222–358) as described in a. c Qualitative comparison of the interaction of AtPHR1222–358 (upper panel) or AtPHR1222–358 Olig1 (lower panel) binding to IRD800-pAtSPX1 in electrophoretic mobility shift assays. Experiment was performed twice with similar results. d–f Quantitative comparison of the interaction of AtPHR1222–358, AtPHR1222–358 Olig1, or AtPHR1222–358 Olig2 with pSPX1 by grating-coupled interferometry (GCI). Sensorgrams show raw data (red lines) and their respective fits (black lines). Table summaries provide the derived association rate (ka), the dissociation rate (kd), and the dissociation constant (Kd).