Figure 5.
p53 can also form unstable foci
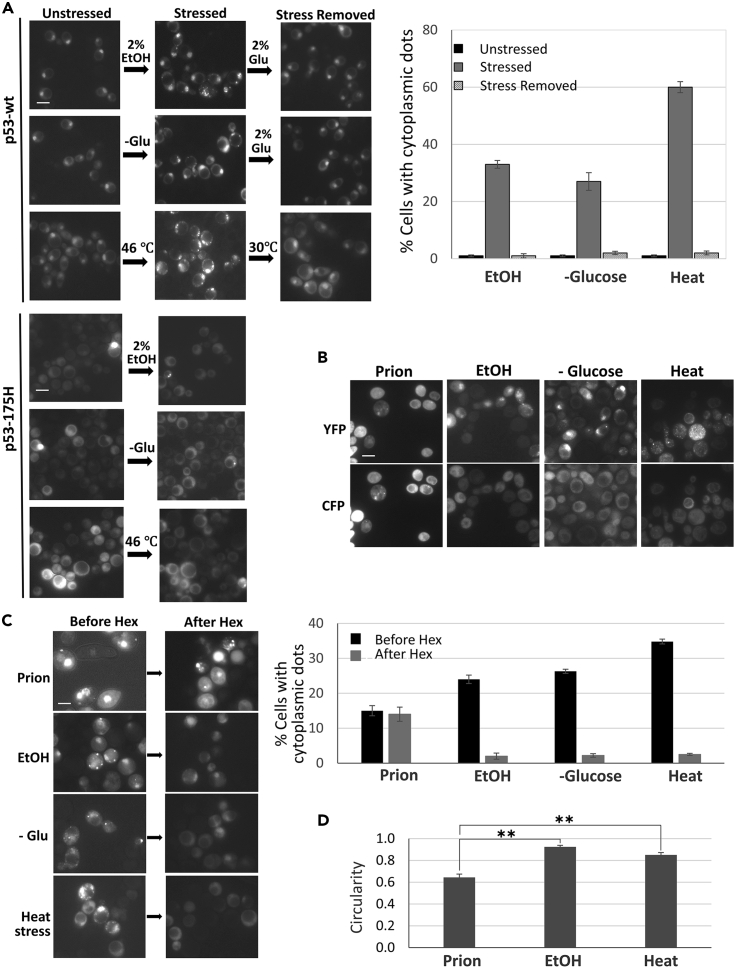
(A) Ethanol, glucose starvation, and heat stress lead to the formation of p53 foci that disappear when the stress is removed. Shown (three upper rows) is yIG397 transformed with pGPD-p53-EYFP grown on plasmid-selective glucose media (left), following stress: 30 min in medium with 2% ethanol, 30 min of glucose starvation or 10 min at 46°C (middle), and then after removal of stress (right). Graph shows the mean of counts from 3 independent transformants ± SEM. Three lower rows show yIG397 transformed with pGPD-p53-175H-EYFP under the same stresses. Arrowhead shows nucleus with foci on top of diffuse fluorescence. Scale bar, 5 μM.
(B) Foci caused by stress do not stain with Thioflavin T. Shown are cells with stress-induced p53-EYFP foci (obtained as in A above) or cells with prion p53-EYFP foci (obtained as in Figure 1E). Cells were fixed, stained with ThT, and examined for EYFP (YFP) fluorescence or ThT staining (CFP).
(C) Hexanediol causes the disappearance of stress-induced, but not prion foci. Shown are cells with stress-induced p53-EYFP foci (obtained as in A above) or cells with prion p53-EYFP foci (obtained as in Figure 1E) before (-Hex) and after (+Hex) 5-min treatments with 10% 1,6-hexanediol. Graph shows counts from three independent transformants ± SEM.
(D) Circularity of stress versus prion foci. Circularity of cytoplasmic aggregates in cells with stress or prion foci obtained as described in (C) (except 15 min of heat was given) was measured. ImageJ and the formula (4 ∗π ∗ area)/perimeterˆ2 was used (n = 40 for each). A value of 1.0 indicates a perfect circular shape, and the lower the value, the less circular the aggregate. Shown are mean ± SEM. ∗∗p calculated with one-tailed t test as <0.005 is shown.
See also Figure S2 and Tables S1 and S2 for a description of strains and plasmids.